Pre-publication of chapter XXV of my forthcoming book “Turkey is Iran and Iran is Turkey – 2500 Years of indivisible Turanian – Iranian Civilization distorted and estranged by Anglo-French Orientalists”; chapters XXIV, XXV and XXVI constitute the Part Ten {Fallacies about the Times of Turanian (Mongolian) Supremacy in terms of Sciences, Arts, Letters, Spirituality and Imperial Universalism} of the book, which is made of 12 parts and 33 chapters. Until now, 8 chapters have been uploaded as partly pre-publication of the book; the present chapter is therefore the 9th (out 33). At the end of the present pre-publication the entire Table of Contents is made available.
Pre-published chapters are marked in blue color, and the present chapter is highlighted in green color.
—————————-

Many people believe that Timur (Tamerlane) was a descendent of Genghis Khan, but this is very wrong; however, he belonged to the same Eastern Turanian Mongolian family as his remote relative who died 109 years before Timur was born (1227-1336). There is actually a distance of 5 generations (the grandfather of the great-grandfather of a person) between the greatest conquerors of Eurasia. However, Genghis Khan and Timur seem to have as common progenitor Genghis Khan’s 4th patrilineal ancestor (the grandfather), who was Timur’s 9th patrilineal ancestor, namely Tumanay Khan.
More specifically, Genghis Khan was son of Yesugei Baghatur son of Bartan Baghatur son of Khabul Khan son of Tumanay Khan. And Timur was son of Taraghai Noyan son of Burgul Noyan son of Aylangir son of Ichil son of Qarachar Noyan son of Suqu Sechen son of Erdemchu Barlas son of Qachuli son of Tumanay Khan. The time passed from the death of Genghis Khan until the birth of Timur (109 years) is approximately the equivalent of the period between the deaths and the births of the following monarchs or spiritual leaders respectively: Consul Crassus’ death and Emperor Trajan’s birth (53 BCE-53 CE), Julian the Apostate’s death and Justinian’s birth (363-482), Nestorius’ death and Prophet Muhammad’s birth (451-571) and Napoleon’s death and Elizabeth II’s birth (1821-1926).

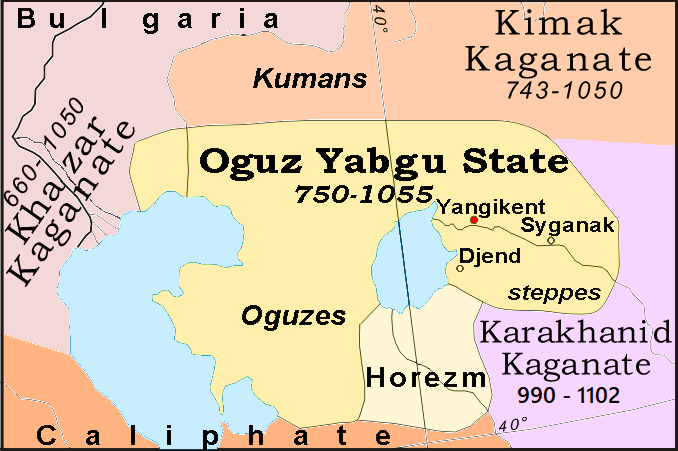
Timur (1336-1405) was born in Shahrisabz (Шаҳрисабз / شهر سبز; Timur’s tomb was built there, but his burial took place at Samarqand), in the southern part of today’s Uzbekistan, close to the border with Tajikistan; at those days, the city was named Kesh. Timur’s family belonged to the Turanian tribe of Barlas, which had recently accepted Islam and become sedentary in Mawarannahr (Transoxiana); those lands were thought to be the epicenter of the legendary and historical Turan, and at the time of Timur’s birth, they were provinces of the Chagatai Empire. About:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Timur
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Barlas
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Shahrisabz
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Timurid_dynasty

Shahrisabz: ruins of Timur’s summer palace, and modern statue
Today, not one scholar raises doubt about the Turanian ancestry and identity of Timur; quite interestingly, and in full refutation of the fallacious Western Orientalist academia, it is Timur himself who rejects this, and by so doing, he gives a lethal blow to the colonially invented distinction between Iran and Turan, to the forged ethnic-linguistic-cultural disconnection of the ‘Turkic nations’ from the ‘Iranian nations’, and to the evil pseudo-universities, institutes and foreign ministries of the colonial Western countries.
Dead before 618 years, Timur speaks to us today through the words that he said personally to the Berber (and not Arab as Western forgers claim) Muslim scholar Ibn Khaldun (1332-1406), whom the great conqueror met during the siege that he laid to Damascus in 1400. When the two greatest men of those days came face to face, they were aged (in their 60s) and already world renowned among all Muslims; the fame of Ibn Khaldun had reached the great conqueror and the magnificence of of Timur’s conquests was known to all the people between the Pacific and the Atlantic. For over a month, the great scholar, who was blocked in the besieged city, was lowered by ropes from the walls of Damascus to encounter Timur. Ibn Khaldun gave extensive details about his daily encounters with Timur in his autobiography (Al-taʿrīf) and in his World History (Kitāb al-ʿibar wa-dīwān al-mubtadaʾ wa-l-khabar fī ayyām al-ʿarab wa-l-ʿajam wa-l-barbar wa-man ʿāṣarahum min dhawī al-sulṭān al-akbar).
Two years before his staggering victory over the Ottomans at Ankara (1402), Timur saved all decent and benign scholars, artists and artisans of Damascus, by evacuating them and dispatching them to Samarqand, and then he sacked the city. There was a significant historical reason for this drastic solution, and Timur duly explained his actions. In fact, he rightfully massacred the entire population in due punishment for the sacrileges earlier perpetrated by the infidel Umayyad caliph Muawiyah, i.e. the murder of Hassan son of Ali (670 CE), and by Yazid I, the son of Muawiyah, namely the monstrous assassination of Husayn son of Ali (680). Ibn Khaldun returned to Cairo to complete his works and wrote exactly what Timur told him about his ancestry.
In total rejection of the Western scholarship’s historical forgery and division between Turan and Iran, the ‘Turanian’ Timur claimed maternal descent from the illustrious ‘Iranian’ (and certainly not ‘Persian’) hero Manuchehr whose legendary deeds were superbly narrated in Farsi poetry by Ferdowsi in his Shahnameh, already 400 years before the encounter of Timur with Ibn Khaldun.

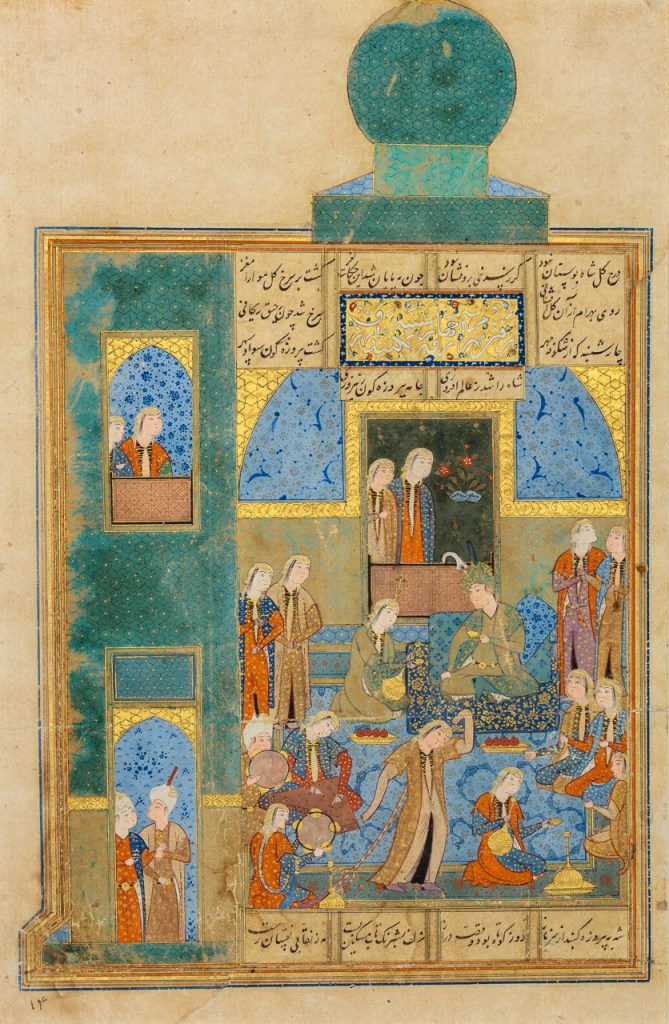
Manuchehr enthroned; from manuscript miniature of Ferdowsi’s Shahnameh
Who is Manuchehr, Timur’s remote ancestor?
Supreme legendary (or apocalyptic-eschatological) king of the Pishdadian dynasty whose first king was the first man Keyumars, Manuchehr is the 7th generation descendent of the founder of the Mankind’s sole royal dynasty. There is no doubt that Ferdowsi’s Shahnameh must have been almost holier than the Quran for Timur, and he definitely knew sizeable portions by heart. The Pishdadian dynasty involves eleven kings of kings: Keyumars, Hushang, Tahmuras, Jamshid, Zahhak, Fereydun, Iraj, Manuchehr, Nowzar, Zaav, and Garshasp. As a matter of fact, Fereydun had three sons, namely Iraj (from Shahmaz, Jamshid’s daughter), Salm and Tur (the latter two from Amavaz, Jamshid’s other daughter).

Manuchehr and Afrasiab fighting against one another; from a 16th c. Shahnameh manuscript
Historical interpretations of the legends superbly narrated in poetry by Ferdowsi offer specific identifications concerning the original ancestors of the three nations that shaped World History: Iraj was viewed as the ancestor of all the Iranians (involving also North Indians and several North Europeans); Tur was considered to be the forefather of all Turanians (Chinese included); and Salm was perceived as the progenitor of all the Anatolians and Eastern Romans (and in general the ‘West’). The three half-brothers represent the mythical-historical stage of division of the surface of the Earth among them.
According to Ferdowsi’s apocalyptic legend, Salm was the firstborn, but being trepid, he avoided fighting with the dragon that attacked him and his brethren; however, the dragon was only his father Fereydun transfigured in order to test his eldest son. On the contrary, Tur’s name means ‘brave’, and this functioned as prophecy. And Iraj was given the worldly glory (termed as ‘Farr’ in Shahnameh and as ‘Khvarenah’ in Avestan, i.e. glow or fortune) as a present granted by God. For this reason, Salm and Tur made a plot and killed Iraj.
At a later stage, Iraj’s daughter gets married with Pashang and their child is Manuchehr, who takes revenge for the assassination of his grandfather. Then, Fereydun (Manuchehr’s great grandfather) abdicates in favor of his great grandson. It is evident that all these ‘events’ take place in an atemporal, spiritual universe, representing values of moral order, hierarchical intelligences, prototypal virtues, choices, deeds and consequences.
However, from that ‘moment’ (Manuchehr’s revenge) started a spiritual clash between the entities ‘Iran’ and ‘Turan’; this clash is prophesied in Ferdowsi’s Shahnameh to end during the ‘reign’ of Kay Khusraw, the 3rd king of kings of the Kayanian dynasty, which was instituted after the termination of the Pishdadian dynasty. It is noteworthy that there is a difference of six (6) generations between Manuchehr and Kay Khusraw, namely Nowzar, Zaav, and Garshasp of the Pishdadian dynasty and Kay Qubad, Kay Kavus, and Kay Khusraw of the subsequent Kayanian dynasty; already Manuchehr’s ‘reign’ is symbolized as of twice perfect duration (120 years: 2×60, as per the sexagesimal system).

Before being extensively narrated and greatly praised in Ferdowsi’s poetry, Manuchehr was an illustrious hero of the pre-Islamic oral traditions; that’s why several rulers were named after this legendary figure. Coin of Manuchihr I, who ruled Fars (Persis) as vassal of the Arsacid Parthian shahs in the early 2nd c. CE (above); (below) coin of Manuchihr III of Persis (late 2nd c. CE)


The name Manuchehr, as part of the Iranian culture, went beyond the limits of the Iranian world and was used by numerous neighboring peoples; Manuchehr khan Enikolopian was an Armenian eunuch of the 18th-19th c. Fath Ali Shah Qajar of Iran.

Jabbar Farshbaf, Manuchehr; a millennia long legend that fascinates the imagination of modern Iranian artists
The above is enough to explain what Timur meant, while specifying to Ibn Khaldun that he was a remote descendant (through his mother’s side) of Manuchehr, i.e. Iraj’s grandson. Timur, a ‘Turanian’, claimed that his ancestry stretched indeed back to the grandson of the forefather of all ‘Iranians’ (Iraj) – and not to Tur, who admittedly was viewed (then and now) as the ancestor of all ‘Turanians’. This automatically means that the two terms were not ethnonyms, and they were perceived totally differently, and not through the distortive lenses of modern rationalism and materialism. In fact, with Timur claiming a clearly ‘Iranian’ origin, the vicious Orientalist distortion and fake division between Turanians and Iranians totally collapses and falls to pieces. About:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pishdadian_dynasty
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fereydun
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Iraj
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tur_(Shahnameh)
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Salm_(Shahnameh)
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Manuchehr
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Kayanian_dynasty
https://iranicaonline.org/articles/aql-e-sork-the-crimsoned-archangel-lit
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ibn_Khaldun
https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/09503110.2016.1198535
https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/23801883.2019.1593089?journalCode=rgih20
https://www.academia.edu/652075/Ibn_Khaldun_His_Life_and_Works

Timur’s military formation, early experience, and rise to power were very different from those of Genghis Khan; the latter spent 20 years in wars against other Eastern Turanian Mongolian tribesmen until he achieved the unification of a certain number of tribes and only after his mid-40s, he went out of the borders of the already unified confederation of Eastern Turanian Mongolian tribes. The former was initially a small band leader, who was engaged in several battles as a mercenary, before allying with different kings (khans) against their opponents.
Originating from the Chagatai Empire, Timur fought along with his khan against the Turanian state of Volga Bulgaria, invaded Khorasan and Khwarazm, increased his basic military force, and then sided with Tughlugh Timur (1329-1363), the khan of Moghulistan (Eastern Chagatai Empire) only to be rewarded with the control of the entire Transoxiana (Mawarannahr). However, very soon, he had to defend that territory against Tughlugh Timur’ son, and his victory helped him consolidate his power. When Timur’s father died, he became a tribal leader, which enabled him to combine military experience and tribal status.

Gur-i Amir (Farsi: گورِ امیر; Uzbek: Amir Temur maqbarasi; ‘the emperor’s tomb’), Timur’s Mausoleum in Samarqand; the historical monument, except for being the burial place of Tamerlane, is one the most prominent architectural masterpieces worldwide as it determined Central Asiatic, Iranian and Indian architecture for many centuries.
Having well studied the History of the Abbasid Caliphate and the stories of the impotent caliphs of the last 350-400 years of Abbasid rule (ca. 850-1258), Timur ruled in the name of the various Chagatai khans, while reducing them to total impotency. Until 1370, Timur managed to establish a strong basis of popular support at Balkh (Bactra, in today’s Afghanistan) and then eliminate his contenders. He then spent considerable time to consolidate his empire. Only after 1380 (and at the age of 45), Timur started becoming a mighty opponent to reckon with beyond the limits of Central Asia. It was then that Timur started his own conquest of the world, thus creating a smaller but surely much more homogeneous empire than that of Genghis Khan.
He first had to defend Khwarazm and Azerbaijan against the powerful Tokhtamysh (1342-1406; Tuqtamış/ Тухтамыш), the khan of the reunified Golden (Blue and White) Horde, Kipchak and Sibir or Siberia (1376-1406). Tokhtamysh had oppressed the uprising of the Turanian Christians of Muscovy (Moscow) in 1382 (there were no Russians at time; they were invented later to set up the Romanov imperial narrative), and squelching the rebellion, he burned the Turanian city of Moscow to the ground. The hostilities between Timur and Tokhtamysh started in the 1380s and the wars culminated in the 1390s.
Timur’s main achievement in the 1380s was the elimination of all the petty dynasties that had surfaced after the decomposition of the Ilkhanate and covered the lands between Euphrates and Syr Darya (Iaxartes). Obliterating divisive statelets, Timur did in the aforementioned vast region what exactly the Ottomans were doing in Western and Central Anatolia and in the South Balkans. These were converging trajectories and one day, sooner or later, the clash between Timur and the Ottomans would come. Timur proved to be merciless in the oppression of rebellions, but his attitude was deliberate. He only wanted to prevent further resistance or opposition. However, he defended and supported the spiritual, academic, educational, artistic and artisan elites, while eliminating indoctrinated religious leaders, stupid sheikhs, tribal contenders, military opponents, and their supporters to the last.

Timur throws a feast in the gardens of Samarqand
By invading Soltaniyeh (in NW Iran) in 1384, Mazandaran (Caspian Sea’s southern coast land), Maragheh and Tabriz (in Iranian Azerbaijan) in 1386, and Isfahan and Shiraz in 1387, Timur controlled the Iranian plateau. Timur’s soldiers executed the quasi-totality of the population of Isfahan (ca. 100000-120000 people). Then, Timur spent several years, asserting his rule throughout the mountains of Zagros, the Caucasus region, and Mesopotamia, and capturing Baghdad in 1393. It was then that Timur rushed to the center of the Iranian plateau to disperse the last Isma’ili remnants that had gathered there again to foment resistance.
During the same period, Timur had to rush to the North; there he reached Western Siberia and Tataria (the western territories of the Golden Horde that constitute today the central part of Russia), defeated Tokhtamysh in the battle of Kondurcha River (1391), burned Ryazan, and invaded all lands around Muscovy (Moscow). This campaign was one of the most remarkable military operations ever undertaken by Islamic imperial armies; Timur’s fast offensive to the North and further on to the West involved an operation of ca. 140000 soldiers, who crossed a distance of over 2700 km, progressing rapidly and for many long hours every day in the formation of a 20 km wide front. So, his soldiers complained that, due to the brief duration of Siberia’s and Tataria’s summer nights, they could not sleep enough between the evening prayer (Isha’a / صلاة العشاء; ca. one hour after the sunset) and the morning prayer (Fajr / صلاة الفجر; ca. one hour before the dawn).
In 1395, Timur returned to the North, after crossing the Caucasus region, and in the famous Battle of Terek River, he won a final victory over Tokhtamysh, destroying Sarai, the Golden Horde capital (near today’s Samara), and Astrakhan. Known as ‘Timur’s stone’, the bilingual {8 lines in Chagatai written in the old Uyghur alphabet (which was directly based on the Aramaic alphabet) and 3 lines in Arabic} inscription found at the Karsakpay mines (Western Kazakhstan) bears witness to the event, and to the commemoration of Timur’s victory, which was also mentioned in historical texts of the period, notably the Zafarnameh (‘book of the victory’) of Sharaf ad-Din Ali Yazdi.
In 1398, Timur turned to the southeast against the Islamic Sultanate of Delhi, which controlled already most of the territory of the modern states of Pakistan, India and Bangladesh; the then ruling Turanian Tughlaq dynasty (1320–1413) had replaced the also Turanian Khalji dynasty (1290–1320), which expanded greatly the territories controlled by the earlier Turanian Mamluk dynasty (1206-1290) that was substituted to the Turanian Ghurid Sultanate (879–1215) and to the Turanian Ghaznavid Empire (977–1186). When Timur arrived in the Delhi region (1398) and the northern parts of what today is confusingly called ‘India’ (instead of Bharat or Hindustan), the majority of the local population was already Turanian of origin, due to successive nomadic migrations, military invasions, extensive clashes, and subsequent amalgamation; and so the local population has been ever since and during the modern times, despite the colonially fabricated masquerade of the fake ‘Indo-European’ India, which is not the name of a real state, but the appellation of a colonial machination based on English perfidy, economic exploitation, political tyranny, historical distortion, and utter academic evilness.
The destruction of many cities in the Indus River valley by Timur’s armies heralded the fall of Delhi, which was one the then world’s richest cities: Tulamba, Multan, and Bhatner were turned to ruins, and no less than 100000 war prisoners were massacred, before the Sultan Nasir al-Din Mahmud Shah Tughluq (1394 – 1413) of the Delhi Sultanate experienced a crushing defeat in December 1398. The sultan of Delhi and his generals counted on the psychological effect that their armored elephants would have on Timur’s soldiers, but their calculations proved to be wrong.
The great conqueror was above all an inventive and resourceful warrior, who knew that even camels can prevail over elephants, if duly and timely utilized by an ingenious strategist; having loaded a great number of camels with straw well tied on them and having supervised the digging of a trench to protect his soldiers, Timur set fire to the camel-borne volumes of straw, when the enemy’s army and elephants attacked. His soldiers pushed the camels forward through use of iron sticks and the flaming camels ran crazily on the elephants, yowling in extreme pain and despair. Thus, Timur’s camels caused unprecedented chaos, hellish fire, and utmost panic to the mammals that smashed under their feet the powerless soldiers of the unfortunate sultan of Delhi.
This was the victory of the camel over the elephant or, if you prefer, the triumph of a conqueror’s intellect over a greedy caretaker’s sloth. Delhi was properly plundered to best finance Timur’s next campaigns, and the entire Bengal, the Ganges River valley, and the Indus River valley became provinces of Timur’s empire or tributary states. About:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tughlugh_Timur
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tokhtamysh
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tokhtamysh%E2%80%93Timur_war
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Karsakpay_inscription
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sharaf_ad-Din_Ali_Yazdi
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Zafarnama_(Yazdi_biography)
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tughlaq_dynasty
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Nasir-ud-Din_Mahmud_Shah_Tughluq
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Khalji_dynasty
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mamluk_dynasty_(Delhi)
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Delhi_Sultanate
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bengal_Sultanate
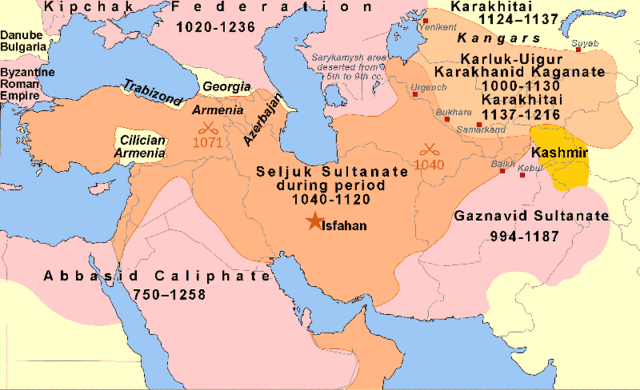
In 1399, Timur turned westwards; after eliminating Haleb (Aleppo) and Damascus, invading the Caucasus region, and demanding submission from the Anatolian Turkmen beys (rulers) in 1399 and 1400, Timur invaded Baghdad in June 1401. The menacing alliance of the Ottomans with the Mamluks of Egypt that had the support of Venice, Genoa and the Knights Hospitaller (who controlled Izmir/Smyrna) created an alarming situation west of Timur’s empire. However, other affairs were top of the priority list for the great conqueror, namely the incessant movements of Turkmen nomads from Central Asia though the Iranian plateau, the Caucasus region, and Anatolia. Timur sided with the Akkoyunlu (آق قویونلو /Aq Qoyunlu / White Sheep confederation – initially centered around Bayburt and known for their frequent intermarriages with Eastern Roman princesses; 1378-1501) and against the Karakoyunlu (قره قویونلو / Qara Qoyunlu /Black Sheep confederation – initially they were Turkmen vassals of the Jalayrid Sultanate in Baghdad and Tabriz; 1374-1468); this was only normal: by connecting themselves with the Ottomans and the Mamluks, the Karakoyunlu caused the ire of Timur.
Within the context of 14th c. Anatolia’s fragmentation, the Ottoman Sultanate appeared to be the strongest state around 1400. But Timur’s viewpoint over the Anatolian affairs was different: he considered the Seljuks as the legitimate sultanate in the entire region, and he wanted to put an order to the Turkmen chaos caused by the numerous progressive migrations. This situation was not only critical for the developments that took then place, but also determinant for what followed, and for the imperial polarization around Anatolia and the Iranian plateau during the 15th – 20th c.
——– Incomparably brilliant & exorbitantly ingenious conquests ——-

Timur enthroned at Balkh

Timur commanding the siege of Balkh

Timur besieges the historic city of Urgench (in Khawarizm/ Chorasmia, today’s Uzbekistan)

Timur about to launch a war against Tokhtamysh

Timur against Tokhtamysh; from a miniature of the ‘Facial Chronicle’ (also known as ‘the illustrated Chronicle of Ivan the Terrible’; Лицевой летописный свод) volume 11, page 251

Timur in the conquest of Baghdad (1393) from a miniature in the Zafarnameh

Timur orders a campaign against Georgia

Timur’s army attacks the remaining survivors in Nerges, Georgia (1396)

Timur’s invasion of India, 1397-1399

The defeat of Nasir Al-Din Mahmum Tughluq at the battle of Delhi 1398

Timur defeats the Mamluk Sultan Nasir-ad-Din Faraj of Egypt

Sultan Bayezid prisoned by Timur, by Stanisław Chlebowski (Станислав Хлебовский; 19th c. Orientalist Russian painter of Polish origin)

Letter dispatched by Timur to Charles VI of France in 1402
————————————————————————————————————
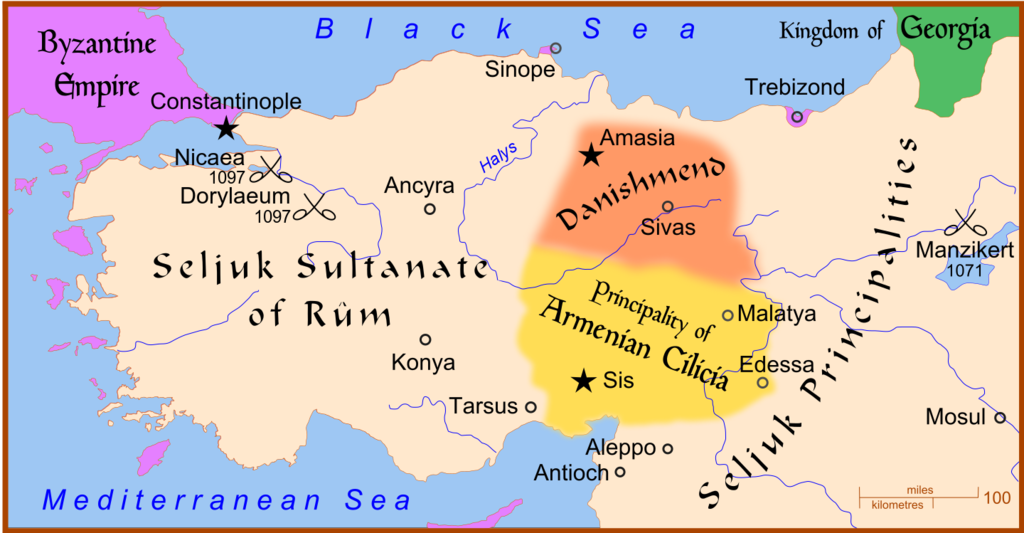
Many people today believe that from the Seljuks to the Ottomans there has been a historical, cultural, spiritual, religious, literary and academic continuity in Anatolia. This is an enormous lie, and Timur’s perfect choice and drastic action help us fully understand how false this impression is. As a matter of fact, between the Seljuks and the Ottomans there was a disruption. About:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Anatolian_beyliks
Timur defeated the Karakoyunlu in 1400; this brought the Akkoyunlu closer to him, and two years later, Timur conceded Diyarbakir to them. This development, in relation with the Ottoman defeat at Ankara in 1402, brought the Ottomans closer to Karakoyunlu and produced an atmosphere of enmity between the Ottomans and the Akkoyunlu. After Timur’s death, the Karakoyunlu managed to oppose successfully the Akkoyunlu for some time, but later the latter prevailed and the former were reduced to a small state in the Caucasus region.
This generated a ferocious rivalry between the then expanding Ottomans and the Akkoyunlu; the latter supported the Central Anatolian Karamanids and effectively stroke an alliance with the Ottoman Empire’s worst enemy, i.e. Venice. The escalation led to several battles between the Ottomans and the Akkoyunlu during the 15th c., and later, with the dissolution of the Akkoyunlu and the absorption of its structures within the rising Safavid Empire (established under the auspices of the homonymous mystical order), the rivalry was transformed into an Ottoman – Safavid quarrel that lasted centuries. But the conflict had basically the traits of an internal Turanian strife that metamorphosed from century to century; the Iranians represented the authentic Turanians, and the Ottomans were the corrupt renegades and the worst enemies of all Turanians. This situation was rectified only in the period 1919-1923, when Kemal Ataturk terminated the Ottoman shame, abolished the ridiculous ‘caliphate’, and reinstated Seljuk-Turanian valor and bravery across Anatolia.
Much discussion has taken place among scholars about the religious motives of all these successive conflicts which were misrepresented as supposed clashes between ‘Sunni’ and ‘Shia’, but this is a lie and there was no religious motivation. In reality, Timur and his successors, the Karakoyunlu, the Akkoyunlu, the Ottomans, and the Mystical Safavid Order were all Muslims, and no ‘Sunni’ – ‘Shia’ distinction applied to them, because simply there is no such distinction; it is a modern colonial academic invention that is not supported by the historical sources.
Even the scholars, who tried ceaselessly to create divisive religious lines where there is none, failed to ‘prove’ that the Karakoyunlu were ‘Shia’, and even if this absurdity could eventually be proven, it would be truly meaningless, because the Karakoyunlu sided with the Ottomans, who are portrayed today as ‘Sunni’ against the Akkoyunlu, who are also depicted as ‘Sunni’ by the fallacious Western academia.
What happened in reality behind all these successive developments was the fact that the internal Turanian strife (between Eastern Turanians and Western Turanians) and the exchange of terrible, written insults between Timur (66 years old at the Battle of Ankara) and Bayezid I (1360-1402; so 42 years old when fighting Timur, which means that there was one generation difference between the two rulers) cast an everlasting shadow on the Ottoman court’s foreign policy making. Then, even worse, Bayezid’s calamitous defeat and humiliating captivity pulled the Ottomans apart from the Turanian world and turned them to the West. Consequently, Ottoman reactions generated further deterioration and conflicts with their main Turanian neighbor, i.e. the Safavid Empire of Iran – which was an entirely Turkic state with almost no Persian population left there anymore. In the Turanian Safavid Empire, Farsi was almost exactly what Medieval Latin was in the Holy Roman Empire of the German Nation: the language of culture and the administration.
It appears odd, but the Timurid Mughal Empire of South Asia (fallaciously described by colonial historiographers as ‘Sunni’) had clearly better relations with Safavid Iran than with the Ottomans as late as 1700, i.e. 300 years after the Battle of Ankara; this delivers a blow to the historical forgery about a ‘Sunni-Shia divide’ which was first invented by colonial academics, then projected onto colonized Muslims worldwide by the colonial administrations, and later repeated pathetically by the postcolonial ignorant, uneducated and idiotic sheikhs, imams, cadis, and muftis.
Every spiritual order and mystical school that was treated well by Timur was viewed suspiciously within the Ottoman territory, and this was not a matter of religious divergence, but of internal Turanian divisions and of imperial rancor. The case of the Safavid Order is quite telling. This mystical order was established before the birth of Osman I (ca. 1255-1323), the ancestor of all Ottomans who belonged to the Kayı tribe of Oghuz Turks. In fact, the Safavid Order was the main emanation of the Zahediyah Mystical Order, which was founded by the Turanian ascetic and mystic Zahed Gilani (1216–1301), a leading spiritual master who was born in the Iranian province of Gilan (southern coast of the Caspian Sea) but originated from Sanjan in Khorasan, a region entirely populated by Turanians at the time. Zahed Gilani was highly revered among the imperial elites of the Ilkhanate. The mystical orders of the Jelveti and the Bayrami are emanations of the Zahediyah Order. Zahed Gilani’s most distinguished disciple was Safi-ad-din Ardabili (1252-1334), an Azeri Turanian who initiated the Safavid Order {named after himself: ‘Safavid’ (صفویه) being an adjective formed out of the name ‘Safi’ (صفی)} as a distinct order although the doctrine was exactly the same as that of the Zahediyah Order.
The holy land of the Safavid Order was Azerbaijan (i.e. the Ancient Iranian holy land of Atropatene), and from there numerous mystics and ascetics traveled across great distances to diffuse the rites of the order throughout the Iranian plateau, Anatolia, Mesopotamia, Central Asia and other Muslim territories. The position of the grand master was hereditary, and after Safi-ad-din Ardabili’s death, his son Sadr al-Dīn Musa (1305-1391) and his grandson Khvajeh Ali Safavi (ca. 1365-1429) oversaw the operations of the order. Timur met Khvajeh Ali Safavi and, although quite older, he was impressed by the spiritual art of the extraordinary mystic; that’s why he treated him well and offered him abundant lands to further finance the expansion of the mystical order. Following this development and the subsequent penetration of the order across the territories of the Timurids and the Akkoyunlu, the Ottomans took an inimical stance toward the Safavid Order and all its spiritual and social ramifications.

Safi ad-din Ardabili in a 16th c, manuscript of the hagiographical text Safvat as-Safa
From the moment Khvajeh Ali Safavi encountered Timur only four generations succeeded one another until Ismail I managed to supplant the Akkoyunlu and establish the Empire of the Safavid Order, which became known as Safavid Empire. These four generations are represented by the Safavid Order’s grandmasters, namely Shaykh Ibrahim (ca. 1400-1447; son of Khvajeh Ali Safavi), Shaykh Junayd (ca. 1410-1460; son of Shaykh Ibrahim), Shaykh Haydar (1459-1488; son of Shaykh Junayd), and Ali Mirza Safavi (also known as Soltan-Ali Safavi; ca. 1475-1494; son of Shaykh Haydar and elder brother of Ismail I, founder of the Safavid Empire). In today’s Azerbaijan and all the peripheral lands (Eastern Anatolia, Iran, and parts of Central Asia), these formidable mystics are highly revered, deemed saints, and constantly venerated, whereas many people bear their names (example: Heydar Aliyev, former president of Azerbaijan).

Tomb of Sheikh Junayd in Khazra, in the northern confines of Azerbaijan

Tomb of Sheykh Heydar in Meshginshahr, Iran

The emblem of the Safavid Order
The Safavid Order grandmasters were Turanian mystics, who reviled the rationalistic and materialistic approaches of the theological circles that held the Ottoman family captive for centuries, therefore generating the ceaseless Turanian fratricide wars only to the benefit of the Pope of Rome and of the Christian Empires of Western Europe. The Safavid Order grandmasters were connected by successive intermarriages with the Timurids, the Akkoyunlu, and the Eastern Romans; for instance, Ali Mirza Safavi was the son of Shaykh Haydar and Alam-Shah Begum (born Martha), who was the daughter of the Akkoyunlu Empire’s most powerful shah, Uzun Hasan, and Despina Khatun (Theodora Megale Komnene).
As they appear to have commanded enormous spiritual powers and performed miraculous deeds, their followers expressed total devotion to them; however, we cannot be absolutely sure about what several contemporaneous historiographers wrote about them at the time, namely that the members of the Safavid Order considered Shaykh Junayd as God Incarnate (‘ilah’) and called his son Shaykh Haydar as ‘Son of God’ (‘ibn Allah’). There were many antagonistic spiritual orders and theological schools at the time, and the clash between esoteric spirituality and rationalistic theology was overwhelming. The rationalistic theologians, who realized their impotency vis-à-vis the spiritual masters of the different Islamic orders, instead of concluding about how far from the essence of the true religion their worthless jurisprudential and rationalistic rhetoric had gone, used inflammatory verbalism, immoral attitude, and malicious defamatory tactics against the grandmasters of the spiritual orders. This practice turned Muslims from living faithful to putrefied carrion.
Of course, the concept of ‘God Incarnate’ is intolerable in Islam, but there are no original sources written by members of the 15th c. Safavid Order about themselves, their noble rites, and their grandmasters; consequently, the then rising rationalistic and materialistic trends among several Muslim theologians may have resulted in total misunderstanding of the Safavid Order’s spiritual terminology, which cannot be comprehended by defective, rationalistic minds. In addition, the jealousy and the envy that several ignorant theologians felt against various renowned spiritual grandmasters make of their literature an untrustworthy libel; an example is offered by Fadl-Allah ben Ruzbehan Qonyi, the legalist and rationalist theologian of the Akkoyunlu court, in his Tāriḵ-e ‘Ālāmārā-ye amini.
About:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Zahed_Gilani
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Zahediyeh
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Jelveti
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bayramiye
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Safi-ad-din_Ardabili
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Safavid_order
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sadr_al-D%C4%ABn_M%C5%ABs%C4%81
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Khvajeh_Ali_Safavi
https://iranicaonline.org/articles/ali-kaja-also-known-as-sayyed-ali-ajami-b
https://iranicaonline.org/articles/jonayd
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Shaykh_Junayd
https://www.academia.edu/4255709/Oghuz_Khan_Narratives
https://iranicaonline.org/articles/haydar-safavi
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Shaykh_Haydar
https://iranicaonline.org/articles/ali-mirza-d
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ali_Mirza_Safavi
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ismail_I
https://iranicaonline.org/articles/esmail-i-safawi
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Uzun_Hasan
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Despina_Khatun
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Kara_Koyunlu
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Aq_Qoyunlu
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Osman_I
The point is that this whole issue goes indeed back to the times of Timur, and the Ottoman enmity toward the Safavid Order first and the Safavid Empire later was only due to the devastating defeat of Bayezid I at Ankara (1402) and to the excellent relationship established between Timur and the Safavid Order’s grandmaster Khvajeh Ali Safavi. The Ottoman – Safavid hostility, which lasted for more than two centuries (and was subsequently inherited by the also Turkmen Afshar and the Qajar dynasties of Iran for almost another two centuries), was of no ethnic and no national character. Both empires were indeed ruled by Turanians, had populations that were Turanian in their majority, and claimed the same ancestry and traditions. Not even one drop of Persian blood could be found in the reins of the Turkmen Ismail I (1487-1524; reign: 1501-1524). In both empires, Turanian (or Turkic) languages were used in the army and the administration, Farsi in poetry, literature, history and culture, and Arabic in sciences (astronomy, mathematics, medicine, natural sciences, geography, etc.). But the Ottomans reacted instinctively to all things Safavid, because even the name of the order reminded them of the humiliating defeat at Ankara in 1402.
The exchange of insults between Timur and Bayezid I involved ethnic denigration; but of course it was an entirely internal Turanian affair. As an Eastern Turanian, Timur rejected the lowly character, mentality and attitude of the settled Western Turanians; and he made his viewpoint bluntly known, fully rejecting assertions and pretensions earlier expressed in arrogant style by the pathetic Bayezid I. In fact, the Ottomans had to stop the blockade of Constantinople and turn the bulk of their forces to the east, because Timur invaded Sivas (Sebasteia) in 1401; arriving at Ankara, the Ottomans were supported by Albanian and Serbian soldiers, who fought along Bayezid’s army, as their states were vassals to the Ottomans.
Timur’s forces slightly outnumbered those of the Ottoman sultan, but this was not the determinant factor for the outstanding victory. Timur was smart enough to allow the Ottomans to advance to the east (reaching Çubuk) and to take an offensive, while part of his army ran fast southwestwards and then turned to the east, thus encircling the Ottomans. Timur counted also on his horse archers, who hit the Ottoman army terribly, and always thinking out-of-the-box, he made sure that his adversaries fail to secure water supply. To do this, some of his auxiliary forces diverted the Çubuk inlet to a reservoir, thus preventing the Ottoman soldiers from access to water; under the Anatolian plateau’s scorching summer sun, this trick had a catastrophic impact on the Ottoman army. To add misfortune to misery, Bayezid I faced desertions of soldiers and officers from his army, notably the Qarai Turks (originating from the Keraite Eastern Turanians) and the Sipahi cavalrymen of the former Anatolian beyliks; these forces joined Timur’s army.
That is why the 20th of July was always a ‘dies nefastus’ (an ominous day) for the Ottomans; actually, it was not only a defeat. It was the only time in the 600-year long Ottoman History when a sultan was held captive and died in captivity. It was also the beginning of the Ottoman interregnum, the civil war among Bayezid I’s sons, which lasted for 11 years (1402-1413). About:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bayezid_I
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Battle_of_Ankara
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ottoman_Interregnum
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Qarai_Turks
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Keraites
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sipahi
After his victory, Timur proceeded to the western confines of Anatolia and invaded Izmir (Smyrna), kicking the Knights Hospitaller out of there. The entire family of Timur fought with him in the West; his sons and his grandsons were engaged in the battle of Ankara. To support the Ottomans and confuse Timur, the Karakoyunlu ruler Qara Yusuf attacked Baghdad, but after the Battle of Ankara, Timur sent forces that recaptured Baghdad under the command of Abu Bakr, son of Miran Shah, Timur’s third son, who was then the older among his two surviving sons. Timur returned to Azerbaijan, Khorasan and Samarqand where he spent some time, planning his next conquests. Since the Yuan dynasty was overthrown in China (1368) and the first emperors of the Ming dynasty expressed an interest to be involved in Central Asia, Timur set up an alliance with Eastern Turanian Mongolian forces in order to attack China. However, marching toward the east, he died in February 1405 at Otrar (also known as Farab; Kangju in Chinese) in today’s Kazakhstan’s southern provinces.
Timur’s succession was not an easy affair, because all the contenders did not agree on the matter. As a matter of fact, two of his four sons had died before him: Umar Shaikh Mirza I (1356-1394) and Jahangir Mirza (1356-1376). Few years before dying, Timur expressed his favor for Jahangir Mirza’s elder son Muhammad Sultan Mirza (1375-1403), but he also died in young age and before his grandfather. Little time before dying, Timur appointed another son of Jahangir Mirza as his successor: Pir Muhammad Mirza (1374-1407); but the heir apparent failed to garner significant support or to control the capital city of the empire, Samarqand.
There were reasons for which Timur did not want any of his two surviving sons to rise to his throne. Miran Shah (1366-1408) had an accident in the late 1380s after having fallen from his horse; this generated a traumatic brain injury and subsequent mental difficulties that were known to many people. Exploiting this situation, the Hurufi mystics (the Hurufiyyah mystical order developed an Islamic system of Kabbalah, crediting letters of the Arabic alphabet with hidden, spiritual value, after the esoteric teachings of Fazlallah Astarabadi; 1340-1394) denounced Miran Shah as the Antichrist (Dajjal), absurdly altering his name to Maran Shah (King of the Serpents). However, Timur’s third son was successful in combating them. The Hurufiyyah were duly dispersed, although some of their erroneous teachings survived among other spiritual orders. The end result is that due to the extensive defamation, Miran Shah’s chances to rule became nil. However, he contributed to the turmoil, because he supported his son Khalil Sultan (1384-1411) as successor to Timur.
Timur’s youngest son, Shah Rukh (1377-1447), was considered as too soft to be an emperor; this was Timur’s publicly expressed opinion. The reality is that Shah Rukh was a man of letters, arts, sciences, trade, diplomacy and negotiations, and that he resorted to war only when no other solution was ostensible. As a matter of fact, Shah Rukh, who was the ruler of Herat and the eastern provinces, claimed the right to his father’s throne, but in modesty and wisdom; he was not urged for a showdown with Khalil Sultan. Having accurately evaluated his nephew’s capabilities, he preferred to let him rule incompetently (as he expected him to do), so that all the people finally turn against him. This process lasted four years (1405-1409); Khalil Sultan ruled indeed as successor of Timur, but he was so incompetent that, when Shah Rukh marched against Samarqand, no one opposed him. As he was not a bloodthirsty conqueror but a wise moralist, he appointed Khalil Sultan as governor of Ray. Shah Rukh ruled for 38 years (1409-1447), contributing to what is now called ‘Timurid Renaissance’ more than his father.
The internal turmoil of the Timurid Empire caused several defeats to Timur’s successors; in 1406 and in 1408, Qara Yusuf of the Karakoyunlu marked two victories over the Timurid forces in Azerbaijan, in the Battle of Nakhchivan and in the Battle of Sardrud; in the latter, Miran Shah was killed and then his body impaled. When Shah Rukh rose to his father’s throne, the western part of the Timurid Empire was lost the Karakoyunlu, the Akkoyunlu and the Ottomans. About:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Umar_Shaikh_Mirza_I
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Jahangir_Mirza_(Timurid_prince)
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Muhammad_Sultan_Mirza
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Miran_Shah
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Shah_Rukh
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pir_Muhammad_(son_of_Jahangir)
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Miran_Shah
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Shah_Rukh
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hurufism
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Khalil_Sultan
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Shahrokh_(mythical_bird)
—————————————
FORTHCOMING
Turkey is Iran and Iran is Turkey
2500 Years of indivisible Turanian – Iranian Civilization distorted and estranged by Anglo-French Orientalists
By Prof. Muhammet Şemsettin Gözübüyükoğlu
(Muhammad Shamsaddin Megalommatis)
TABLE OF CONTENTS
PREFACE
CONTENTS
PART ONE. INTRODUCTION
CHAPTER I: A World held Captive by the Colonial Gangsters: France, England, the US, and the Delusional History Taught in their Deceitful Universities
A. Examples of fake national names
a) Mongolia (or Mughal) and Deccan – Not India!
b) Tataria – Not Russia!
c) Romania (with the accent on the penultimate syllable) – Not Greece!
d) Kemet or Masr – Not Egypt!
e) Khazaria – not Israel!
f) Abyssinia – not Ethiopia!
B. Earlier Exchange of Messages in Turkish
C. The Preamble to My Response
CHAPTER II: Geopolitics does not exist.
CHAPTER III: Politics does not exist.
CHAPTER IV: Turkey and Iran beyond politics and geopolitics: Orientalism, conceptualization, contextualization, concealment
A. Orientalism
B. Conceptualization
C. Contextualization
D. Concealment
PART TWO. EXAMPLE OF ACADEMICALLY CONCEALED, KEY HISTORICAL TEXT
CHAPTER V: Plutarch and the diffusion of Ancient Egyptian and Iranian Religions and Cultures in Ancient Greece
PART THREE. TURKEY AND IRAN BEYOND POLITICS AND GEOPOLITICS: REJECTION OF THE ORIENTALIST, TURKOLOGIST AND IRANOLOGIST FALLACIES ABOUT ACHAEMENID HISTORY
CHAPTER VI: The fallacy that Turkic nations were not present in the wider Mesopotamia – Anatolia region in pre-Islamic times
CHAPTER VII: The fallacious representation of Achaemenid Iran by Western Orientalists
CHAPTER VIII: The premeditated disconnection of Atropatene / Adhurbadagan from the History of Azerbaijan
CHAPTER IX: Iranian and Turanian nations in Achaemenid Iran
CHAPTER X: Iranian and Turanian Religions in Pre-Islamic Iran
PART FOUR. FALLACIES ABOUT THE SO-CALLED HELLENISTIC PERIOD, ALEXANDER THE GREAT, AND THE SELEUCID & THE PARTHIAN ARSACID TIMES
CHAPTER XI: Alexander the Great as Iranian King of Kings, the fallacy of Hellenism, and the nonexistent Hellenistic Period
CHAPTER XII: Parthian Turan: an Anti-Persian dynasty
CHAPTER XIII: Parthian Turan and the Philhellenism of the Arsacids
PART FIVE. FALLACIES ABOUT SASSANID HISTORY, HISTORY OF RELIGIONS, AND THE HISTORY OF MIGRATIONS
CHAPTER XIV: Arsacid & Sassanid Iran, and the wars against the Mithraic – Christian Roman Empire
CHAPTER XV: Sassanid Iran – Turan, Kartir, Roman Empire, Christianity, Mani and Manichaeism
CHAPTER XVI: Iran – Turan, Manichaeism & Islam during the Migration Period and the Early Caliphates
PART SIX. FALLACIES ABOUT THE EARLY EXPANSION OF ISLAM: THE FAKE ARABIZATION OF ISLAM
CHAPTER XVII: Iran – Turan and the Western, Orientalist distortions about the successful, early expansion of Islam during the 7th – 8th c. CE
CHAPTER XVIII: Western Orientalist falsifications of Islamic History: Identification of Islam with only Hejaz at the times of the Prophet
CHAPTER XIX: The fake, Orientalist Arabization of Islam
CHAPTER XX: The systematic dissociation of Islam from the Ancient Oriental History
PART SEVEN. THE FICTIONAL DIVISION OF ISLAM INTO ‘SUNNI’ AND ‘SHIA’
CHAPTER XXI: The fabrication of the fake divide ‘Sunni Islam vs. Shia Islam’
PART EIGHT. THE DISTORTED TERM ‘PERSIANATE’
CHAPTER XXII: The fake Persianization of the Abbasid Caliphate
PART NINE. FALLACIES ABOUT THE GOLDEN ERA OF THE ISLAMIC CIVILIZATION
CHAPTER XXIII: From Ferdowsi to the Seljuk Turks, Nizam al Mulk, Nizami Ganjavi, Jalal ad-Din Rumi and Haji Bektash
PART TEN. FALLACIES ABOUT THE TIMES OF TURANIAN (MONGOLIAN) SUPREMACY IN TERMS OF SCIENCES, ARTS, LETTERS, SPIRITUALITY AND IMPERIAL UNIVERSALISM
CHAPTER XXIV: From Genghis Khan, Nasir al-Din al Tusi and Hulagu to Timur
CHAPTER XXV: Timur (Tamerlane) as a Turanian Muslim descendant of the Great Hero Manuchehr, his exploits and triumphs, and the slow rise of the Turanian Safavid Order
CHAPTER XXVI: the Timurid Era as Peak of the Islamic Civilization, Shah Rukh, and Ulugh Beg, the Astronomer Emperor
PART ELEVEN. HOW AND WHY THE OTTOMANS, THE SAFAVIDS AND THE MUGHALS FAILED
CHAPTER XXVII: Ethnically Turanian Safavids & Culturally Iranian Ottomans: two identical empires that mirrored one another
CHAPTER XXVIII: Spirituality, Religion & Theology: the fallacy of the Safavid conversion of Iran to ‘Shia Islam’
CHAPTER XXIX: Selim I, Ismail I, and Babur
CHAPTER XXX: The Battle of Chaldiran (1514), and how it predestined the Fall of the Islamic World
CHAPTER XXXI: Ottomans, Safavids and Mughals: victims of their sectarianism, tribalism, theology, and wrong evaluation of the colonial West
CHAPTER XXXII: Ottomans, Iranians and Mughals from Nader Shah to Kemal Ataturk
PART TWELVE. CONCLUSION
CHAPTER XXXIII: Turkey and Iran beyond politics and geopolitics: whereto?
————————————————————————————–
Download the chapter (text only) in PDF:
Download the chapter (with pictures and legends) in PDF: