За пределами афроцентризма: предпосылки для того, чтобы Сомали возглавила африканскую деколонизацию и девестернизацию
What follows is the quasi-totality of my response to a Somali scholar, intellectual and activist, who happened to be a very good personal friend since the early 2010s and my days in Somalia. Being a perspicacious reader, my good friend, who originates from two different tribal backgrounds and has an unmatched knowledge of his great but recently (since 1991) beleaguered nation, noticed several recent articles of mine in which I call for a definite and irreversible replacement of the Anglo-French colonial rule in Africa with a genuine, secular African-Chinese-Indian-Russian alliance.
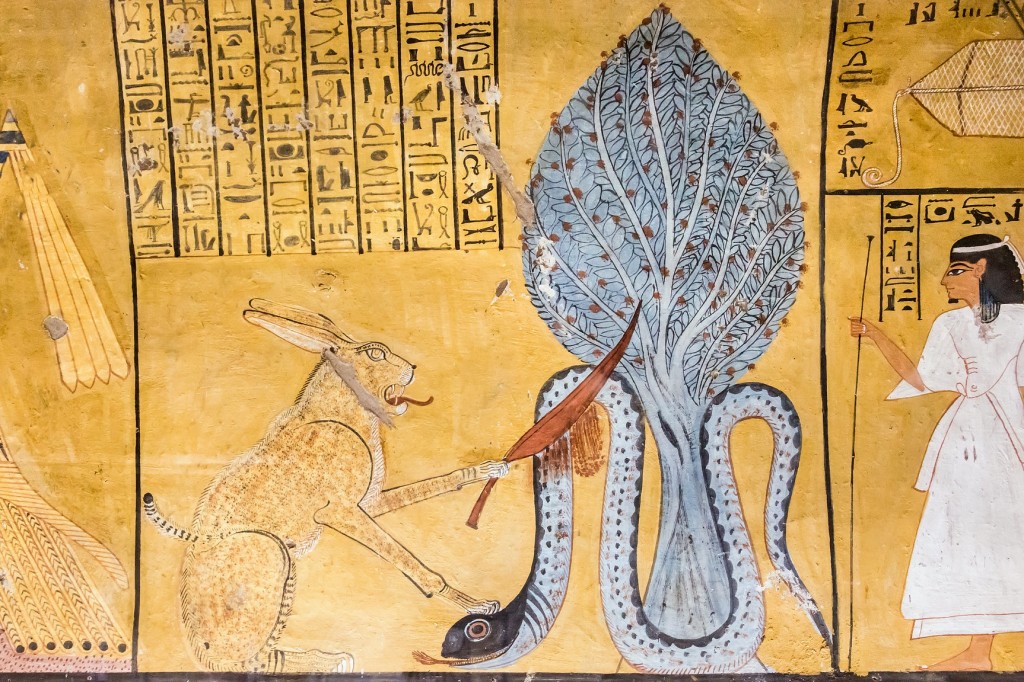

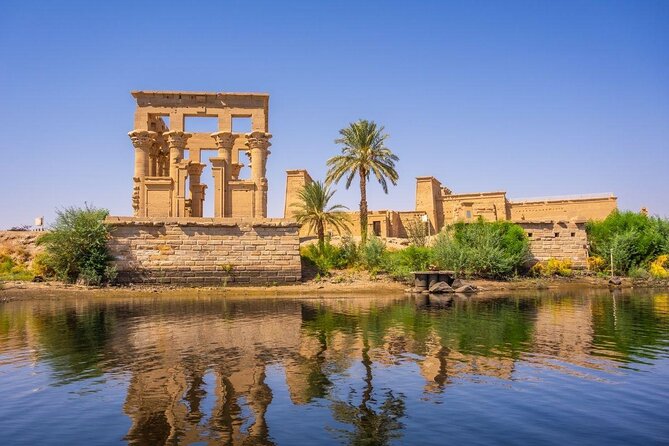
The Great Cat – Horus (Messiah) defeats the Ancient Serpent – Seth (Anti-Messiah); wall painting from the Tomb of Pashedu (TT3) in Deir el Medina (Luxor West) Afrocentrism will be a total failure if it is thought to be just an African intellectual’s thought, idea, theory or ideology. Theorizing is already part of Western intellectuals’ falsehood and evildoing. Philosophy is nonsensical, absurd, false and inhuman. There was never ‘philosophy’ in Africa, because it would be viewed as deviation and decay. Contrarily, in Ancient Africa there were Truth, Transcendental Spirituality, Primordial Myth, World Conceptualization, Supratemporal Eschatology, and Spiritual-Material Synergy. So, the primary tasks of African Afrocentric intellectuals involve the irrevocable obliteration of all Western terms and their replacement with Oriental African concepts, notions, terms, values and virtues. Consequently, there cannot be “an Afrocentric University”, because this term follows a Western pattern. Offering herewith an example, I suggest that every institution in which African students will learn the truth should be called after the Ancient Egyptian term “the Place of Truth” and the instructors “Servants in the Place of Truth”. This title was associated at the time with all the great scholars specializing in mummification and in the preparation of the human soul for the Hereafter. However, this has always been the value of life, learning and knowledge according to all the varieties of African culture: material life is subject to moral judgments that enable us to gain eternal life.
Содержание
Введение
I. Деколонизация и отказ афроцентрической интеллигенции
II. Афроцентристским африканским ученым следовало бы отобрать египтологию у западных востоковедов и африканистов.
III. Западная узурпация африканского наследия должна быть отменена.
IV. Афроцентризм должен был включать в себя резкую критику и полное неприятие так называемой западной цивилизации.
V. Афроцентризм как форма африканского изоляционизма, проводящая линию разделения между колонизированными странами Африки и Азии.
VI. Общая оценка человеческих ресурсов, времени и необходимых затрат
VII. Деколонизация означает, прежде всего, деанглификацию и дефранкизацию.
Contents
Introduction
I. Decolonization and the failure of the Afrocentric Intelligentsia
II. Afrocentric African scholars should have been taken Egyptology back from the Western Orientalists and Africanists
III. Western Usurpation of African Heritage must be canceled.
IV. Afrocentrism had to encompass severe criticism and total rejection of the so-called Western Civilization
V. Afrocentrism as a form of African Isolationism drawing a line of separation between colonized nations in Africa and Asia
VI. General estimation of the human resources, the time, and the cost needed
VII. Decolonization means above all De-Anglicization and De-Francization

——-

———

———-

———–

————-

Molefi Kete Asante
Introduction
Realizing what is at stake and being well acquainted with earlier African attempts for a final decolonization (notably the intellectual-academic sphere of Afrocentrism and the political activists of African Renaissance), my friend, who has the same age with me and who studied, lived, worked and prospered in the USSR, Canada, Yemen and Pakistan, wrote to ask me how Somalia could eventually contribute to or lead the African decolonization and de-Westernization movement, thus taking the Black Continent to the next stage and justifying the great expectations that were created across Africa back in 1960, due to the independence and the unification (of only two out of the five parts) of Somalia.
At this point, I have to add that the present response is only the first of three letters that I planned to send to my friend. The urgent need for worldwide decolonization and de-Westernization has become a major issue for great nations, organizations and alliances, like the BRICS+. Many people across the world would therefore question the entire conversation, stating that presently Somalia is too small, too weak, and too disunited in order to possibly undertake international tasks that seem to be best suited rather to some of the world’s leading states.
I believe that, although this approach may be shared by many people, it is ostensibly very shallow. This is so because stronger a nation is, more difficult it becomes for their rulers, elites, and people to undertake an in-depth self-criticism, reassessment, and restart or partly rectification. In other words, a better organized nation is by definition more conservative and therefore less inclined to changes; these traits and conditions have been attested repeatedly throughout History.
Consequently, when it comes to colonization and Westernization, self-scrutiny must be very deep, and this -at the national level- can be extremely painful. That is why, in Russia, de-Westernization will be a far more difficult process to be carried out than in India.
Taken into consideration that Westernization (not only behavioral-cultural but mainly educational-academic-intellectual) is tantamount to alteration, corruption and degeneration, one has to underscore at this point that national identity is not necessarily proportionate to national independence. It is quite possible that an educationally-academically-intellectually corrupted nation, although in possession of an independent state, has minimal national consciousness (because of their entirely Westernized education), whereas an enslaved nation struggling to achieve national independence may have fully preserved their national identity and intellectual originality.
Back in January 2021, I explained exactly this to an Oromo friend, who wrote to ask me why Egypt does not help the Oromo liberation movements achieve national independence for Oromia and in the process demolish the obsolete and genocidal state of Abyssinia (Fake Ethiopia). Egypt is an independent state without national consciousness of historicity whereas the Oromos are a non-independent nation with emphatically strong Cushitic national identity and cultural originality. It took me a series of five articles to fully respond at the time; in the last article of the series, one can find titles of and links to the earlier parts:

—————–

Innocent C. Onyewuenyi
I expand on these topics, because there is a multitude of parameters in the much needed effort of African decolonization and educational-academic-intellectual de-Westernization. To offer an example, I have to say that even the nefarious term “university” (from the Latin “universitas”) cannot be possibly accepted by all those who -in Africa, Asia, Eastern Europe and Latin America- seek decolonization, de-Westernization, and restoration of the ancestral values, moral standards, cultural integrity, and academic-educational traditions. This is however discussed in a second letter dispatched to my friend. Last, in a third letter, I examine a number of major issues around which the refutation of the Western colonial forgery and pseudo-historical doctrine will have to revolve.
———————- Letter to a Somali friend ———————–
Thank you for the opportunity you offer me to write down my observations, perceptions, reflections, and conclusions on the topic under discussion!
I. Decolonization and the failure of the Afrocentric Intelligentsia
Several educational, academic, intellectual and political efforts have been undertaken over the past six (6) decades in order to take Africa out of the disastrous and heavy, colonial impact and to help the various nations of the Black Continent achieve national identity, cultural integrity, and ultimate liberation from the Western yoke.
Explaining why the Afrocentric African intellectuals failed (or at least they did not meet the early enthusiastic expectations) necessitates an extremely lengthy treatise the size of an encyclopedia; however, at this moment, I have to pinpoint the crucial mistakes made by the leading figures of the movement that became known as Afrocentrism.

————————

————————–

—————————–

Martin Bernal

———————-

—————————

Donald Malcolm Reid
It is crucial to notice that the two most formidable hits against the racist Western pseudo-historical narrative were delivered by defiant Western scholars who rejected, at least partly, the lies of the Eurocentric historical dogma and denounced the evil, discriminatory, anti-African and anti-Islamic manner in which Orientalist disciplines were formed and developed, namely Martin Bernal and Donald Malcolm Reid. This fact demonstrates that Afrocentric intellectuals need to stop theorizing and start an in-depth study of the upended disciplines of the Western Orientalists, which have to be rejected point by point. Further theorizing and more intensified propaganda will damage Afrocentrism; Africans need not to be apologetic. Africa did not need philosophy because Africans had transcendental knowledge, spiritual mastership, moral command, and foremost wisdom. All these crucial dimensions of human superiority were missing among the so-called Greeks, Romans and the other European barbarians, who still needed to search for wisdom (being ‘philos’ to ‘sophia’) and, in the process, they created ‘philosophy’; unfortunately, they failed to go beyond. Today’s Western scholars have to face the reality: either you are able to build pyramids after the Ancient Kemetian (Egyptian) method or you are talking nonsense, only to later label it ‘philosophy’. Consequently, wider intellectual exploration, deeper academic investigation, stronger educational effort and social-governmental concertation will help Africans come up with fresh results and groundbreaking conclusions. All African schoolchildren need therefore to get a solid background in all the Ancient African civilizations.
To offer beforehand a recapitulative judgment, I would say that they all viewed their tasks within a far narrower context, thus minimizing the extent of the work that lies ahead.
They did not realize the importance of inter-African concertation, reciprocal knowledge, and systematized cooperation.
They failed to evaluate the extent to which they all have been altered, Westernized, and alienated from their t=roots.
They did not examine how sick, absurd, criminal, and inhuman the Western world was – even before colonizing Africa and other parts of the world.
And they did not consider as their priority to contact other colonized nations in Asia, Eastern Europe, and Latin America, to exchange descriptions of common experience, and to decide about their much needed common struggle and decolonization effort.
II. Afrocentric African scholars should have been taken Egyptology back from the Western Orientalists and Africanists
First and foremost, their overall mental and intellectual endeavor was utterly wrong, misplaced, upended, and factitious. Although this statement seems to be extremely disappointing and perhaps even unfair, it is not. When people like Cheikh Anta Diop and Molefi Kete Asante decided to oppose the colonial powers and their historical distortions by means of Afrocentrism, they acted (without even understanding it) as typical Western intellectuals or philosophers.

To be effective and fruitful, Afrocentrism must stay close to the historical reality. Western standards of Marketing do not promote the African culture in any sense; on the contrary, they contaminate, corrupt and exterminate it. Afrocentrism is at the antipodes of Modernity – or it is false.

The Afrocentric African intellectuals thought that their own African culture could give them the foremost insignia of originality, but this was a wrong assumption. Unfortunately, they never questioned their authenticity and they failed to notice that they had already been exposed to overwhelming colonial impact at the mental, intellectual, educational, academic and scientific levels. So, they did not even imagine that they had first to methodically filter their mindsets, concepts and beliefs, and to remove the clutter. They did not realize that they had first to thoroughly study in-depth Egyptian hieroglyphics, Ancient Egyptian civilization, and the History of Egypt down to Modern Times in order to have access to the foremost African past.
This would not be an easy task, because they would have to take Egyptological courses mainly in French- or English-speaking countries (or alternatively in Italy, Germany, Russia, Austria, Poland or Egypt – without however major differences in the syllabus, methodology or approach). In these countries’ academic institutions, their professors would teach and propagate the compact, pseudo-historical dogma, which has progressively covered all sectors of Humanities and which was geared in order to historically legitimize and consolidate the Western colonial power at the educational, intellectual, and academic levels. This Western historical forgery is at the origin of every colonial evildoing, because it stipulates the preposterous Western supremacy, it defines the cruel and inhuman West as ‘the realm of civilization’, it denigrates all the other great nations (not only Africans) as barbarians, and it offers to the Western gangsters the foremost pretext to colonize the world.

Denderah, Temple of Hathor; relief with representation of the cosmological doctrine of Khemenu (today’s Ashmunein; Hermupolis in Ancient Greek) that the Ancient Greeks described as ‘Ogdoad’; the basic concept of the Hermupolitan religion is monotheistic.

From the Book of Going Forth by Day, which has been misleadingly named ‘Book of the Dead’ (by Western Egyptologists); version saved in the Papyrus of Ani. Whereas Anubis is represented as weighing the heart of the deceased Ani in the lower part, in the upper section, we see the representation of the cosmological doctrine of Iwnw (Heliopolis in Ancient Greek) that the Ancient Greeks described as ‘Ennead’. The basic concept of the Heliopolitan religion is monotheistic.

Ramesses III represented as making offerings to Ptah, Skhmet and Nefertem, who are also known as the Memphitic Triad, basic element of the cosmological doctrine of the polytheistic priesthood of Memphis. The Hermupolitan, Heliopolitan and Memphitic religions were the oldest and most widespread Ancient Egyptian religions during the 3rd and the 1st half of the 2nd millennium BCE. With the rise of the 18th dynasty in the 16th c. BCE, Egyptian monotheism and polytheism clashed under the forms of Atonism (or Atenism) and Amun Theban Triad; the Theban theology was mainly a readjustment and reformulation of the Memphitic religion, whereas Aton consists in a most stressed form of the Heliopolitan monotheism.

Amun, Mut & Khonsu: the Theban Triad
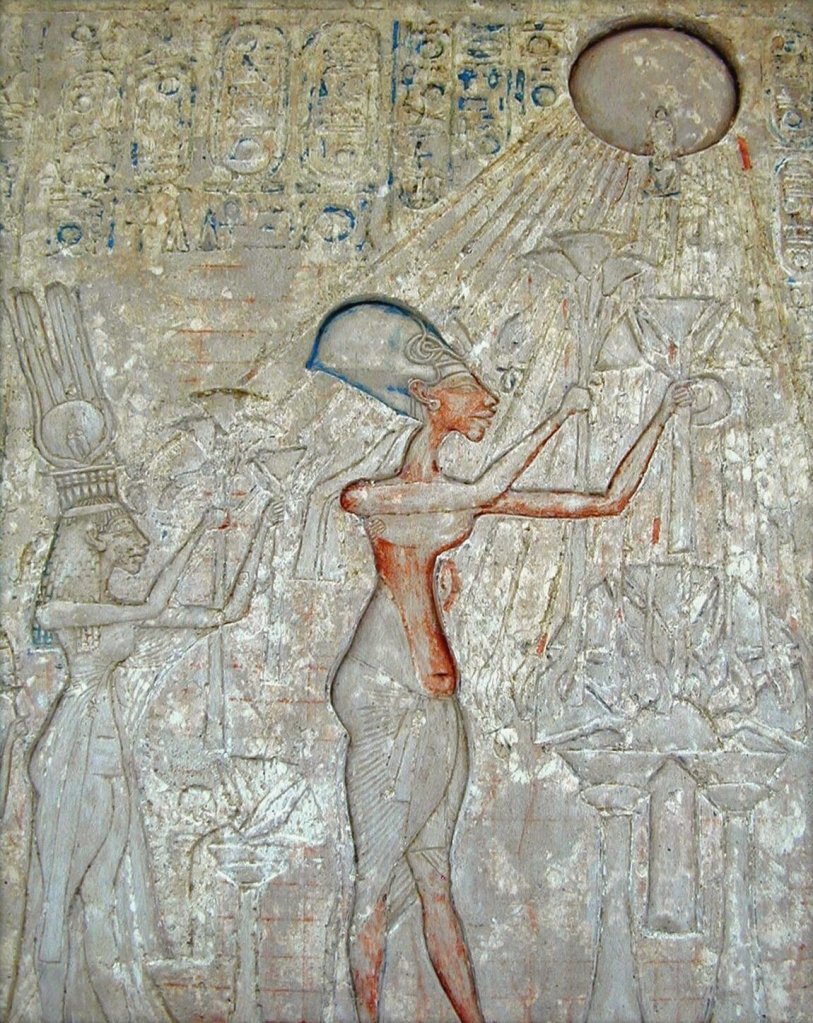

Royal tomb of Tel Amarna (Akhetaton), the new capital founded by the monotheist Pharaoh who broke with the polytheistic past of Thebes of Egypt; relief representing Akhenaten and Nefertiti adoring Aten

The Great Hymn to Aten, composed by the great African mystic and pharaoh Akhenaten, constitutes African History’s holiest text and the earliest monotheistic written document worldwide; the extraordinary text consists in one of the numerous and solid proofs that demonstrate the fallacy of the Biblical narrative, the Egyptian identity of the populations that are said to have left Kemet (Egypt) under Moses, and the Egyptian origin of the Biblical Psalms. As a matter of fact, what is nowadays called as Biblical (or Hebrew) religion is nothing more than Egyptian monotheistic religiosity in Canaanite language and in monotheistic Assyrian imperial-universal context. Epitome of African spirituality, the Great Hymn to Aten must become the founding text of the national education in every African state.
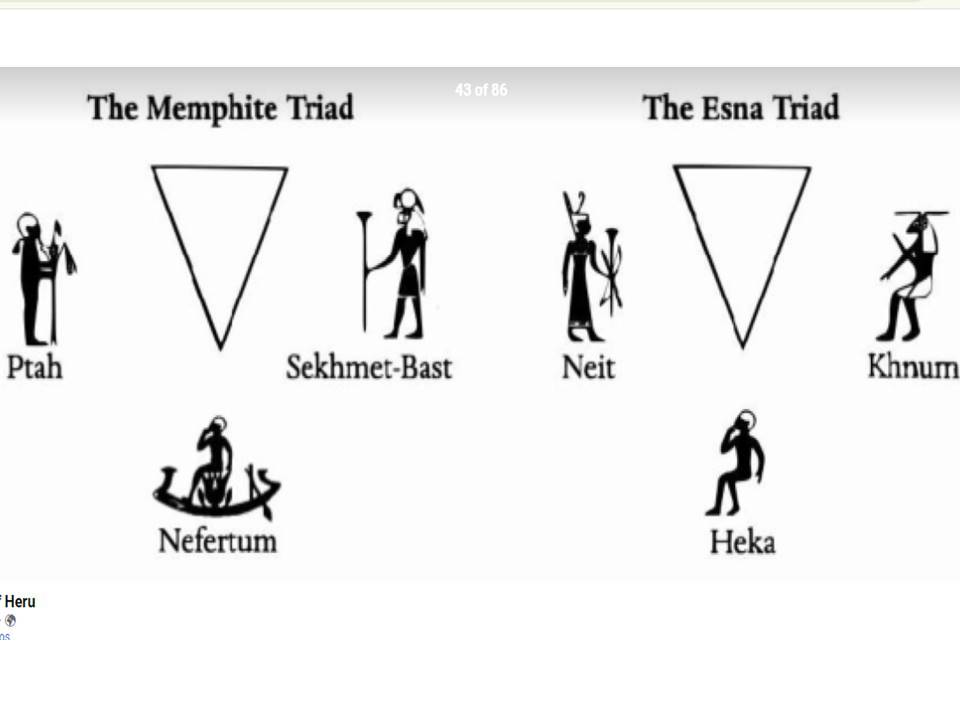
Religious confrontation, opposition to other dogmas, rejection of counterfeit doctrines and elimination of opposite faiths and cults seldom took the form of civil war in Ancient Egypt; they customarily involved reformulation of earlier concepts, transformation of fundamental notions, subordination of divinities to a strongly promoted deity, assimilation of divine traits into those of another divinity, oblivion of previously eulogized traits, introduction of new divine virtues, reference to an unfathomable yet beneficial mystery, and restructuring of the overall outline of faith. A typical example was the inception (3rd c. BCE) of the Esna Triad around Khnum, Neith and Heka; this was an Upper Egyptian monotheistic effort to undermine the impact of the Memphitic theology across the country.

————————-

————————–

There is not a single concept, notion, idea or narrative stated in Ancient Greek philosophical texts that does not originate from one of the aforementioned Egyptian religions, forms of spirituality, and theological schools.
So, as Afrocentric African students, they would have to meticulously search, find out, and identify -in the manuals that they would study and in the courses that they would attend- endless inaccuracies, deliberate errors, obvious lies, and a multitude of techniques geared by Western Egyptologists in order to distort the historical truth and to adjust all newly found data to the arbitrarily preconceived and shamelessly pronounced diagram of World Pseudo-History that the evil intellectuals of Western European Renaissance composed in the 15th and the 16th centuries, before sending their heinous, anti-Christian, barbarian and racist conquistadors and rascals to invade the rest of the world and carry out unstoppable series of genocides.
This means that, instead of blindly accepting their Western professors’ assumptions and teachings, the Afrocentric African students of Western Egyptologists should scrutinize every single word, argumentation, conclusion, pretension, interpretation, lecture and publication of their professors, denounce -point by point- every single case of falsehood or deliberate distortion, and reject the Western Egyptology across the board.
The task of the first Afrocentric African Egyptologists would be immense, involving
a) the publication of encyclopedias and books, academic periodicals, and secondary education manuals, and
b) extensive activities in terms of science popularization in newspapers, reviews, movies and TV programs – all available in many African languages, not in French and English.
All the criminal lies of the Western Eurocentric Egyptologists should be ferociously denounced, whereas Egypt, Sudan and Libya should be persuasively asked by all the other African states to effectively ban every Western European, Australian, and North American Egyptologist and Egyptological mission member, who did not denounce the fallacies of Eurocentrism, Judeo-Christian tradition, Greco-Roman civilization, Hellenism, Classicism and Renaissance.
To give you an approximate idea, if the aforementioned development had taken place at the time, by now there would have been formed several hundreds of Afrocentric African Egyptologists teaching factual, truthful and unadulterated Egyptology in more than a hundred universities across the Black Continent. You certainly can fathom what a devastating blow against the Western European and North American colonial academia this development would have been.
Contrarily to this indispensable task and inevitable priority, the first Afrocentric African Egyptologists were merely theorizing in a most harmless manner, while having a very shallow understanding of Ancient Egypt. As a matter of fact, they never challenged, let alone endangered, the academic, educational and intellectual interests and biases of the Western colonial elites. Even worse, they intended to make political use of the Ancient Egyptian heritage; but this was really calamitous because “politics” is an entirely Modern Western fabrication that did not exist in the past in Africa, Asia or Europe. There will never be decolonization with politics anywhere, because there was no politics before the colonial era.
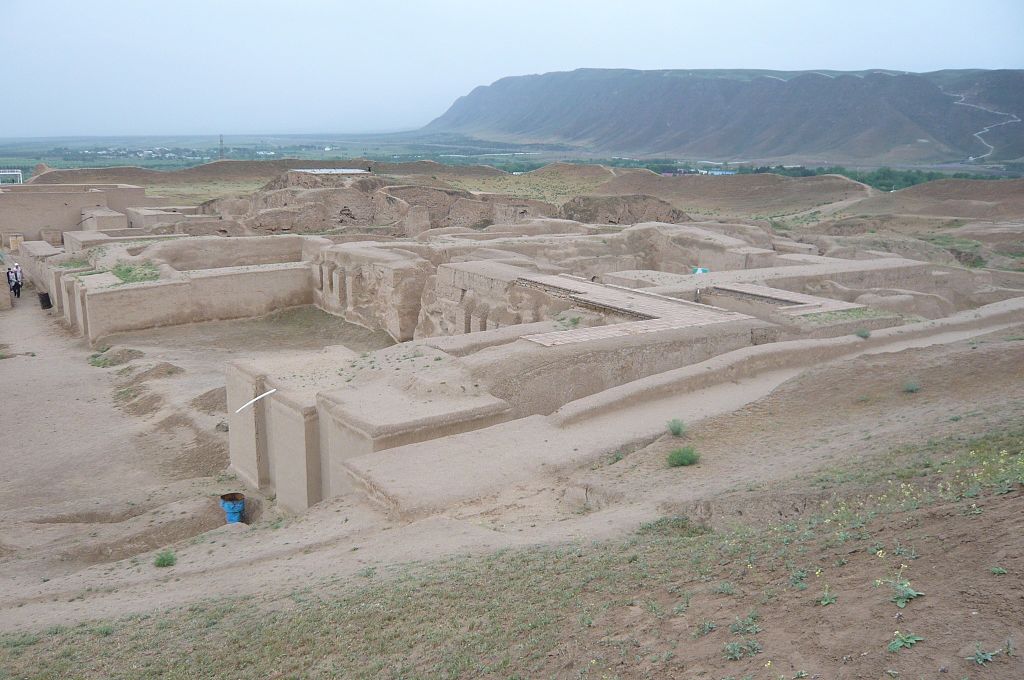
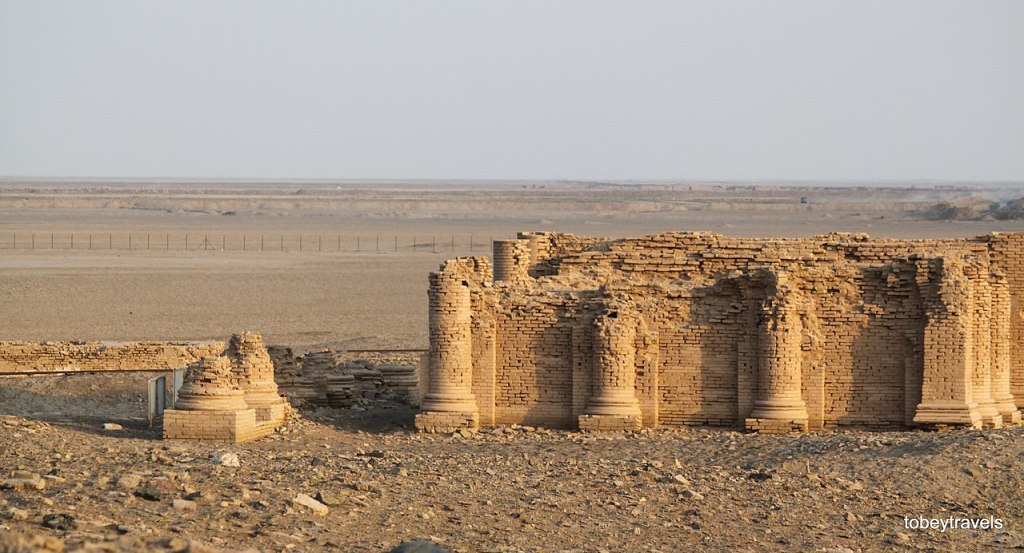
More importantly, the aforementioned approach, which applies to Egyptology, should have also been followed in all the other sectors of Humanities that concern Pre-Islamic Africa, namely Meroitic-Cushitic Studies, Axumite Abyssinian Studies (to best document the Yemenite, non-African, origin of the Axumites), Punt and Ancient Somali Studies, Punic (Carthaginian) Studies, Libyco-Berber Studies, Late Antiquity Africa, and African Christianity.
III. Western Usurpation of African Heritage must be canceled.
In addition to the aforementioned, the Afrocentric African Egyptologists should undertake another, turly enormous endeavor, namely the ultimate denunciation and the irrevocable cancellation of the Western usurpation of a sizeable part of African and Asiatic historical heritage. Example:
Plotinus (204-270), who was an Egyptian mystic, erudite scholar, and spiritual master, has been distortedly named as “Greek Platonist philosopher” by the racist, colonial forgers of Western universities; but Plotinus was born in today’s Asyut (Zawty in Egyptian Hieroglyphics; Syowt in Coptic; Lycopolis in Ancient Greek) in Central Egypt. He was an Egyptian, and his spiritual doctrine was entirely Egyptian; Plotinus wrote in Ancient Greek only to further propagate his knowledge, wisdom and world conceptualization, but his knowledge of Ancient Egyptian Hieroglyphics is unquestionable.
Would it be therefore normal to consider an African American as an Anglo-Saxon only because he writes in English?
Many non-specialists may wish to formulate another question about Plotinus:
Why do then Western forgers call Plotinus “a Platonist philosopher”?
This is simple to answer.
Plato had traveled and studied in Egypt; in fact, his theories and world views are not his, but have derived from well-known, fundamental Ancient Egyptian concepts of transcendental knowledge, spirituality, moral, and world conceptualization. The underlying nature of Plato’s so-called philosophy is the Ancient Egyptian Iwnw (Heliopolitan) dogma (also called among Greeks as “the Ennead”), i.e. one of the most influential religions of Ancient Egypt, which progressively spread throughout the Mediterranean Sea and Europe. So, Plotinus is a valuable part of Ancient African heritage that has been usurped after it was labeled “Greek” by the racist and criminal French, English and American academics and forgers.

———————-

Above: this is what existed in Plotinus’ mind about the Soul. Below: and this is what exists in the minds of Western authors about Plotinus’ conceptualization of the Soul.

Another example is offered by Porphyry of Tyre (234-305), Plotinus’ student; he was a Phoenician spiritual master, cosmologist, mathematician, intellectual, debater, and author. Although Assyrian-Babylonian spirituality, science and wisdom are evident in his works, Western academic fraudsters still call him “Neo-platonic philosopher”, which is another blatant case of Western usurpation of Oriental Asiatic heritage.

This is what existed in the mind of Porphyry of Tyre about the Tree of Life {relief from the palace of Ashurnasirpal II (884-859 BCE) at Kalhu (today’s Nimrud).
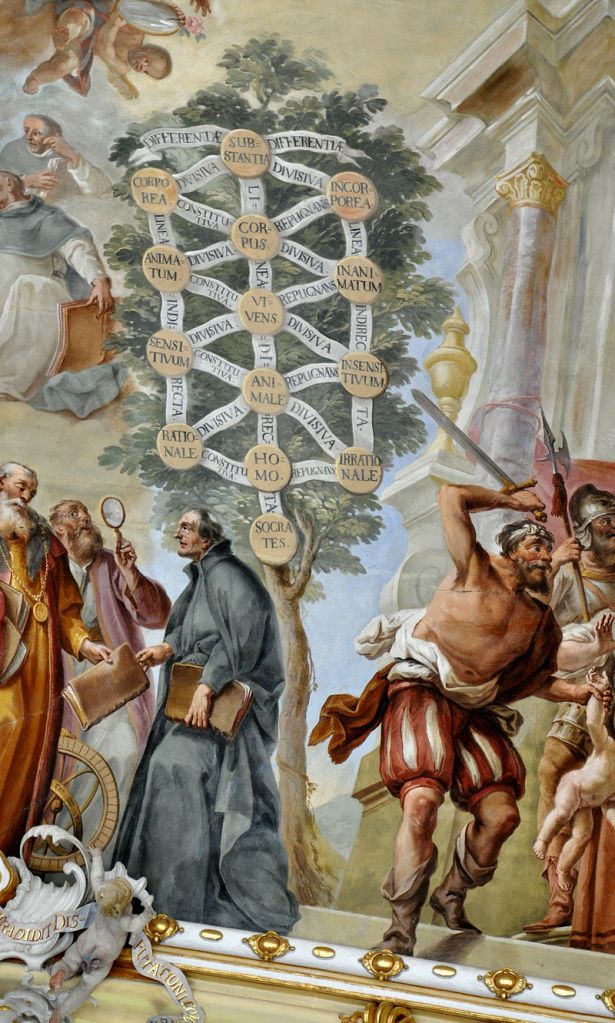

And this is what the 18th c. ignominious Catholic monks of the Premonstratensian Order thought (due to their Baroque fallacy and arrogant absurdity) that Porphyry of Tyre believed that the Tree of Life could possibly be: a linear nonsense {from the Schussenried Monastery (Bad Schussenried, Baden-Württemberg, Germany), New Convent Building: Library Hall ceiling fresco}.
There is nothing “Greek”, nothing “European”, and nothing “Western”, in the highly valuable works of those great spiritual mystics and erudite scholars; they were genuinely Oriental, either African or Asiatic. But faithless, atheist, and materialist forgers of the Western universities have ludicrously labeled all these great masters “philosophers”, thus propagating the use of a profane word, which during the Antiquity was of low connotation, because it was in straight opposition to words such as “wise”, “sacred”, “venerated”, “pious”, and “consecrated”.
Compared to the high priests of Egypt, Cush/Meroe, Punt/Somalia, Carthage, Phoenicia, Assyria and Iran, the so-called Ancient Greek and Roman “philosophers” constituted villainous and degenerate evildoers. The profanity of those corrupt, obscene and barbarian malefactors (like the Epicureans) is beyond description, as they pretended that Man has the right to perform all the absurd crimes and the most repugnant sins if this is ‘good’ for his sensual pleasures.
No Afrocentric African Egyptologists and Africanists will ever do good service to the Black Continent, their national identity, their cultural integrity, and the values and virtues of their ancestors, if they do not irrevocably reject the Western usurpation of Oriental heritage; actually, it is their obligation to irreversibly eradicate the last shred of Western impact on African education, academic knowledge, intellectual life, and moral tradition.
IV. Afrocentrism had to encompass severe criticism and total rejection of the so-called Western Civilization
Second, the overall mental and intellectual endeavor of the Afrocentric African intellectuals was definitely incomplete. Not only they did not study Egyptology to acquire access into the Ancient Egyptian Hieroglyphic sources that constitute the utmost African originality, but they also failed to duly explore, analyze and criticize the Modern Western world. All the same, they would have two major tasks in this regard; more specifically, they had to first, evaluate the Western world on the basis of their own African criteria and values, and second, publish their argumentations, evaluations, and conclusions.
As a matter of fact, they had to ultimately investigate the so-called Western world per se, identify its nature and origin, describe the process of its fabrication, denounce its unreliability and inhumanity, and discredit the Western intellectuals’ conclusions, assumptions, pretensions, and fake stories. In other words, they had to effectively check whether the so-called Western world was anything more than spiritual corruption, deliberate alteration, and degenerate disfigurement of a part of the Ancient Oriental world.
This is a very critical point; although no Afrocentric African Egyptologists and Africanists have been formed until now (in order to subsequently re-establish an Afrocentric version of Egyptology and of several other related fields of Humanities), African universities have been flooded with numerous types of absurd, preposterous Western propaganda, notably the academic fields of French Literature, Art, History and Culture, English Literature, Art, History and Culture, Italian Literature, Art, History and Culture, Modern European Philosophy, etc.
All these fields have been accepted and developed in African universities; and the contents of numerous syllabuses were instructed to African students on African soil. This was carried out very thoughtlessly and extremely disastrously. Due to this situation, a great number of texts written by Western poets, playwrights, authors, philosophers and others were diffused among African populations. This means that immoral concepts, evil plots, inhuman stories, criminal ideas, vicious thoughts, counterfeit values, and execrable vices made their way into the hearts and the minds of millions of innocent Africans, fully corrupting them and effectively destroying their culture. This very deceitful and extremely pernicious method made many Africans unconsciously accept what would be impermissible for their parents’ and ancestors’ standards, values, and measures to tolerate.
It is most unfortunate that the Afrocentric intelligentsia of Africa failed to make it clear that no Western European and Northern American text can be taught, studied, printed or diffused on African soil, if it does not comprehensively comply with African values, virtues and traditions. Voltaire, Jean Jacques Rousseau, William Shakespeare, François Rabelais, Joachim du Bellay, Montesquieu, Victor Hugo, Charles Baudelaire, Rudyard Kipling, Albert Camus, Agatha Christie, and scores of other supposedly important, valuable or even acceptable authors are absolutely pathetic and worthless when evaluated as per African moral values, measures and cultural criteria.

Although the libretto was written by the then leading Egyptologist, the renowned Auguste Mariette, Giuseppe Verdi’s Aida (commissioned by Cairo’s Khedivial Opera House and premiered on 24th December 1871) is a colonial hallucination that reflects all the Orientalist distortions of African History; more specifically, Aida was said to be an Ethiopian princess, but this was a multiple fraud, because at the time no one could identify the location with Sudan, namely the Ancient Kingdom of Cush, because the Ancient Greek term ‘Ethiopia’ had fallen in desuetude. Even worse, inter-African wars (between Egypt/Kemet and Ethiopia/Cush – not to be confused with Abyssinia) are at the epicenter of the plot. This reflects the numerous conflicts and clashes between the 25th (Cushitic) and the 26th (Libyan) dynasties of Ancient Egypt, which took place between the 9th and the 6th c. BCE, when Egypt was continually divided into several kingdoms. This opera generates therefore a sad and nefarious impression about Africa to the audience.

Similarly, Verdi’s Nabucco (from Ancient Greek ‘Nabucodonosor’/’Nebuchadnezzar’ in Ancient Hebrew), which was composed in 1841, at a time the Assyrian-Babylonian cuneiform sources had not been deciphered, consists in mere projection of Western Freemasonic and Zionist clichés onto a purely fictional story that distorts the Ancient History of Mesopotamia, while also villainously insinuating that the Ottomans were the descendants of the Babylonians, which is absurd. These forms of Western racist art systematically denigrated all the Oriental nations involved, criminally reducing them to the position of subaltern pupils and servants.
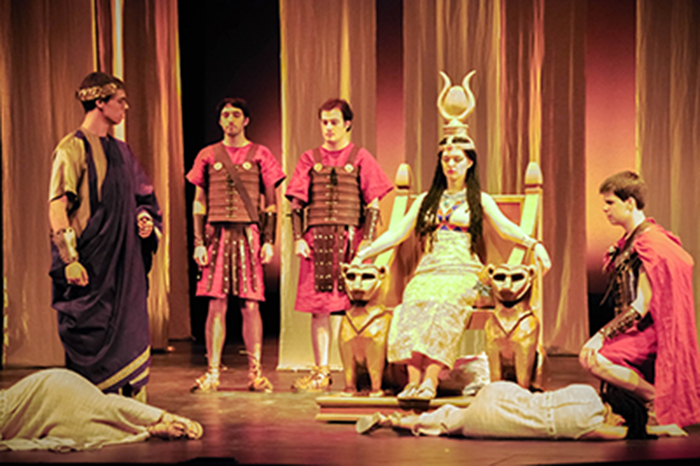

Written in the first years of the 17th c., William Shakespeare’s play ‘Antony and Cleopatra’ is a multi-layered distortion of factual truth and historical sources. The extraordinary denigration of the Egyptians, as carried out throughout the text, makes of the playwright an anti-African pamphleteer. The selective use of Plutarch’s Life of Antony (from the Parallel Lives) fully demonstrates the real, ignoble intentions of Shakespeare who wanted to plainly indoctrinate his compatriots in anti-Egyptian and anti-African odium. Depicting Egypt as a sensual environment and Rome as an austere social context, Shakespeare convinces us that he did not have a clue about how the everyday life was in either country 1600 years before he wrote the notorious play.
In fact, most of these pathetic, anomalous and evil individuals were heinous fanatics, paranoid fraudsters, and abhorrent sinners, who carried out crimes, propagated evildoing, despised their fellow countrymen, and promoted immoral manners and unethical behavior. They were abnormal to the extent of loathing and reviling the Christian culture of the societies in which they belonged and which they wanted to destroy. Clearly, there is only one reason for which Agatha Christie’s novels (to offer an example) could be accepted as a study topic in African universities: in order to castigate the evil plot and to articulate a devastating critique of English Literature on the basis of African moral considerations, traditional values, and literary standards.

Agatha Christie’s ‘Death on the Nile’ (pictures from John Guillermin’s movie – 1978) is an insult against every average Egyptian and African; the only indigenous character, Mr. Choudhury, is portrayed as an idiot and as a humble admirer of his colonial masters.

V. Afrocentrism as a form of African Isolationism drawing a line of separation between colonized nations in Africa and Asia
Third, the overall mental and intellectual endeavor of the Afrocentric African intellectuals proved also to be disturbingly egocentric; this is due to the fact that the interpretation of their approach leads us to the conclusion that they considered the colonial wrongdoings as necessary to eliminate only from Africa. In other words, they failed to notice that Africa was only one of the colonial powers’ targeted lands or continents and that the Spaniards, the Portuguese, the English, the French, the Dutch, and the Belgians also colonized vast territories in Asia, Europe and Latin America. Last, they did not take into account that the Western colonial practices have been continued by several derivative states of the colonial powers, notably the US, New Zealand, Australia, and Canada.
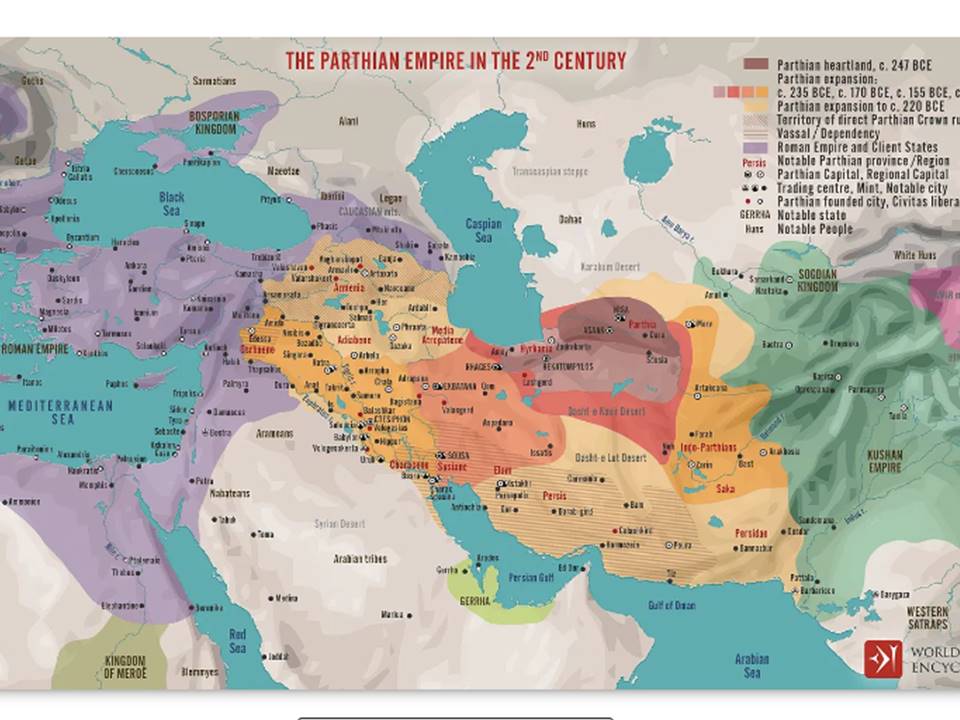
It would however be very helpful for all the Afrocentric African intellectuals to examine how the Ottoman Empire (one of African History’s largest empires), Iran, the Mughal Empire of India, China, and even Russia were systematically and incessantly targeted by the colonial empires of the West. Furthermore, it would be very useful for those intellectuals to observe and assess that, for the colonial powers, the military occupation or the political dependence of a land, nation or kingdom is not the only means of effectively impacting a colony and introducing it into the colonial metropolis’ sphere of influence.
Russia was never occupied militarily by the Western colonial powers, but from the beginning of the 18th c., the Romanov dynasty was targeted with a sophisticated and multifaceted process of Westernization (Europeanization) to which many Russian nobles, clerics and intellectuals reacted ferociously. It is quite telling that the Imperial Russian elite was successfully dragged to the extent of becoming an ally of the atheist and profane state of France (instead of naturally siding with Germany and Austria-Hungary), only to be exhausted in WW I, defeated by the Germans, and replaced by the Communists, who were totally alien to Russian culture.
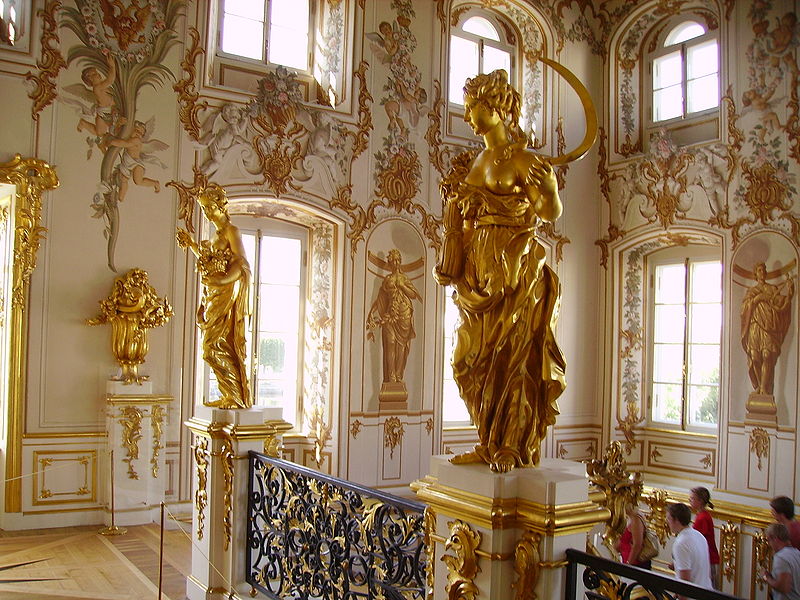

Although they were exceedingly lavish, the Peterhof Palace’s decorative artifacts (here you see one part of the Grand Staircase) were a stupendous insult against the average Russian’s culture, traditions, education, and faith. In brief, the phenomenal palace was a Western outpost inside the Christian Orthodox Empire of the Romanov dynasty. This would inevitably bring about the collapse of the Russian imperial state, which lacked cultural-intellectual homogeneity due to the Westernization of its elites.
This shows that to best serve African nations’ interests and anticolonial vocation, the Afrocentric intelligentsia of Africa should enlarge their horizons, see Africa as only one colonially targeted land or continent, and enrich their knowledge and experience with the study of non-African civilizations, lands and nations that have also been colonized by the Western colonial powers. No one can possibly assess the historical distortions made by the Western academics during the formulation of their bogus-historical dogma, without duly delving into numerous fields of Humanities and fully checking endless inaccuracies, deliberate errors, obvious lies and a multitude of techniques geared by Western scholars in fields like Assyriology, Hittitology, Iranology, Biblical Studies, Indology, Islamology, Turkology, Slavic and Russian Studies, and Sinology.
VI. General estimation of the human resources, the time, and the cost needed
The aforementioned criticism may now help as a guideline for the future; what was not achieved in the past can be attempted now. Presently, perhaps the international context is more favorable to such an effort. Speaking for a middle-size African state, such as Algeria (in guise of an example), the effort to launch numerous sectors of Humanities, as new academic fields entirely free of colonial falsehood and distortion, would not be difficult to undertake. All the same, it would certainly demand perfect conceptualization of the commendable objective and proper contextualization within the international community. As it consists in a project of national and all-African dimensions, it should be placed under central (governmental) guidance and supervision.
It goes without saying that a project this important would also involve fully committed students, who would be absolutely conscious of the national and all-African character of the undertaking, and of their role in it. They should first be prepared during a 3 or 4-year syllabus (leading to a B.A.) and then financially supported during their graduate, postgraduate and doctoral studies. They should finally be committed to
a) returning to their ‘alma mater’,
b) being appointed there, and
c) launching a new department of studies in the sector in which they would have already been specialized.
To give an estimate, this national and all-African project (covering sectors named or insinuated in the aforementioned parts II, III, IV and V) would encompass around 50 (fifty) different sectors of Humanities. Selecting 10 (ten) genuinely interested and devoted students, who would be ready to specialize in the designated fields and return to be employed, means a total of 500 students, i.e. 500 scholarships for 10 years, and one secretariat in order to adequately administer the whole project. For a country like Eritrea or Mauritania, this would certainly be difficult to undertake, but for Algeria it is affordable. It would not exceed 100 million US$ for the entire period (including also the infrastructure and the establishment of basic libraries).
———————————————————-
Colonization in Africa will continue until all African schoolchildren study -amongst other sites and monuments- in their schools and learn -in their languages- about the following:
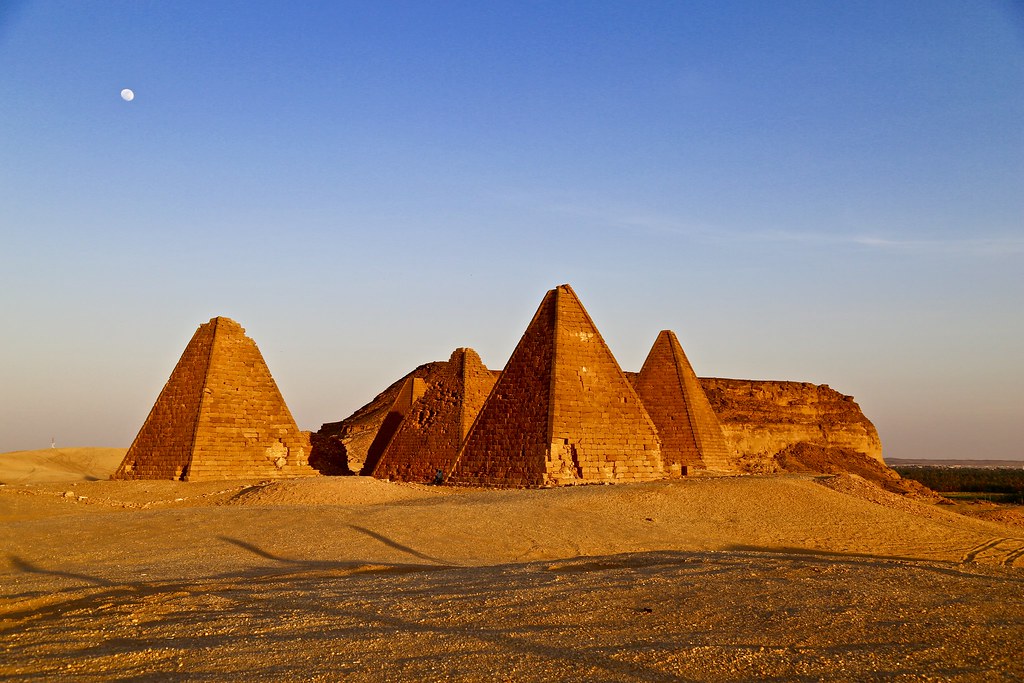

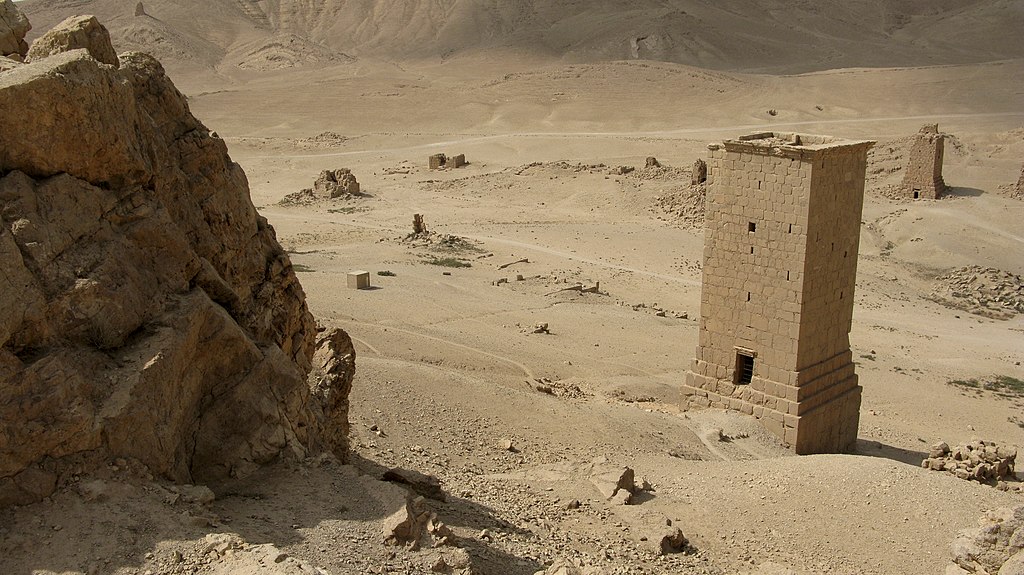
Above: Napata, the capital of the kingdom of Cush (Ancient Ethiopia / unrelated to the state of Abyssinia, today’s Fake Ethiopia) in today’s Karima-Sudan; called today Jebel Barkal, the holy mountain of Amun was for all Egyptian and Sudanese adepts of the Theban Triad the world’s holiest place. Below: the Cushitic necropolis of El Kurru, ca. 15 km from Karima/Napata.

———–
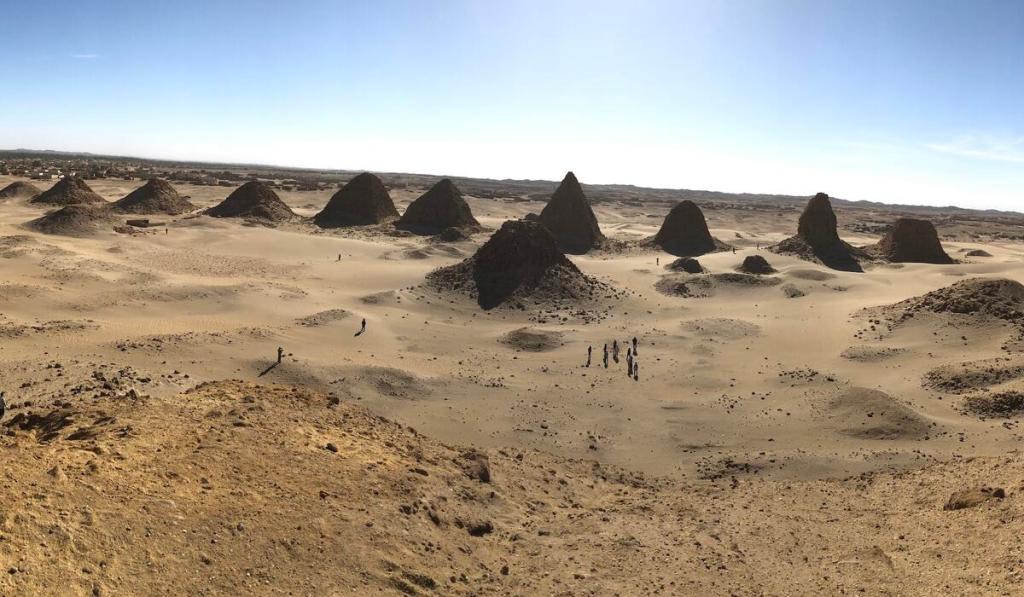

Nuri, on the other side of the Nile, opposite Karima/Napata: the third Cushitic necropolis
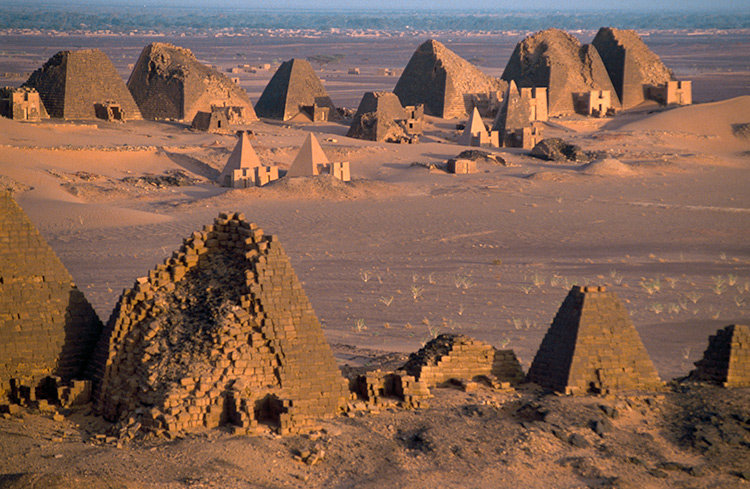

Mjrwjwit-Meroe: late Cushitic capital

Meroe, capital of Cush (Ethiopia) from the 5th c. BCE until 360 CE, attracted the admiration of Romans and Greeks; when the Armenian king Tiridates I visited Nero in Rome (66 CE), the Roman Emperor organized an extraordinary spectacle with Meroitic gladiators in his honor, which means that the Ancient Sudanese impressed the Romans without being however impressed by them. Three centuries later, the Phoenician Heliodorus from Homs (Emesa, in Syria) wrote an extraordinary account of Meroe in his “Aithiopica” (in the middle of the 4th c. CE). Meroe proved to be invincible and impregnable until the Abyssinian Axumite king Ezana invaded it around 360 CE (attacking from the southeast). After a brief period of Axumite occupation, three Christian kingdoms emerged in the area of today’s Sudan: (from North to South) Nobatia, Makuria and Alodia (or Alwa) – all unrelated to Axum, which collapsed with the arrival of Islam. The southernmost kingdom was the last to fall (around 1500); it was invaded by the Funj (African Muslims), who attacked from Sahara.

————————————————

Naqa: a major religious center of the Meroitic Kingdom
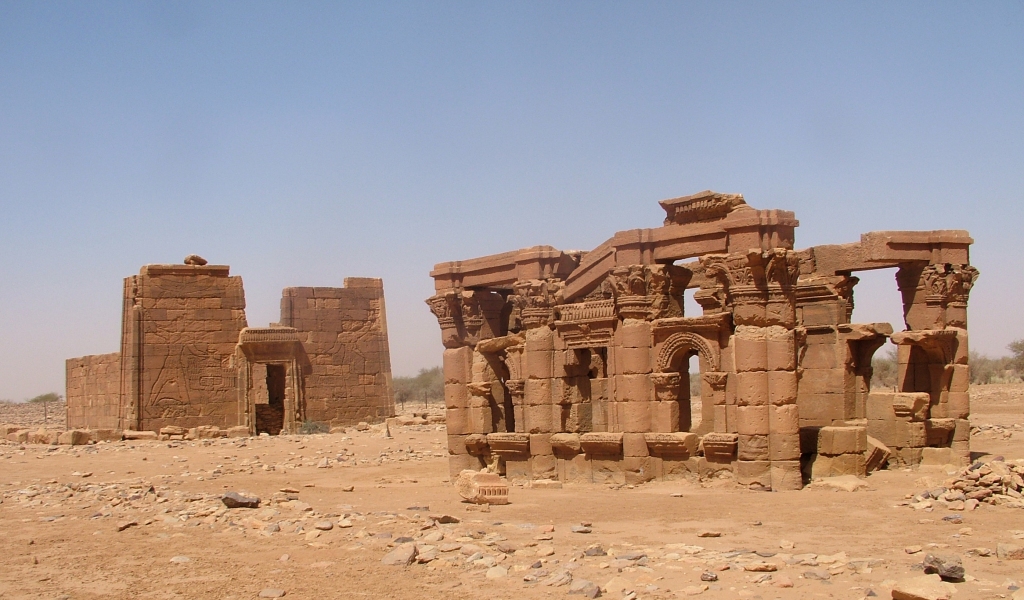

Nsqa

Mussawarat as-Sufra: a major imperial and religious center of the Meroitic kingdom; it is located deep in the Butana, Sudan’s eastern desert, which is demarcated by the Blue Nile, the United Nile, Atbara River (affluent of the Nile) and the mountains alongside the Sudanese-Abyssinian(‘Ethiopian’) borders.
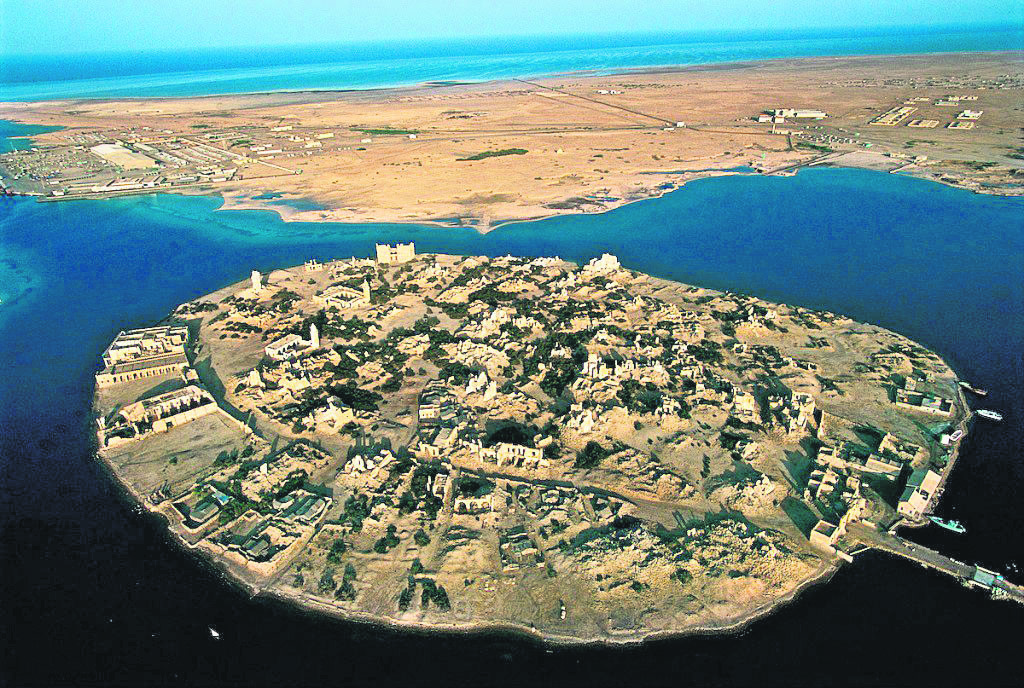

Suakin-Ptolemais Theron: a Ptolemaic colony and port-of-call on the Red Sea coast of today’s Sudan; Ptolemais Theron (lit. Ptolemaic harbor of the Hunters) was quite significant for the trade between the East and the West. That is why it was mentioned in the historical text ‘Periplus of the (‘Erythraean’) Red Sea’, which was written by an anonymous author in the 2nd half of the 1st c. CE. The site retained its historical importance and, after the 13th c., it became the gate to Mecca for African Muslims willing to perform hajj (pilgrimage).
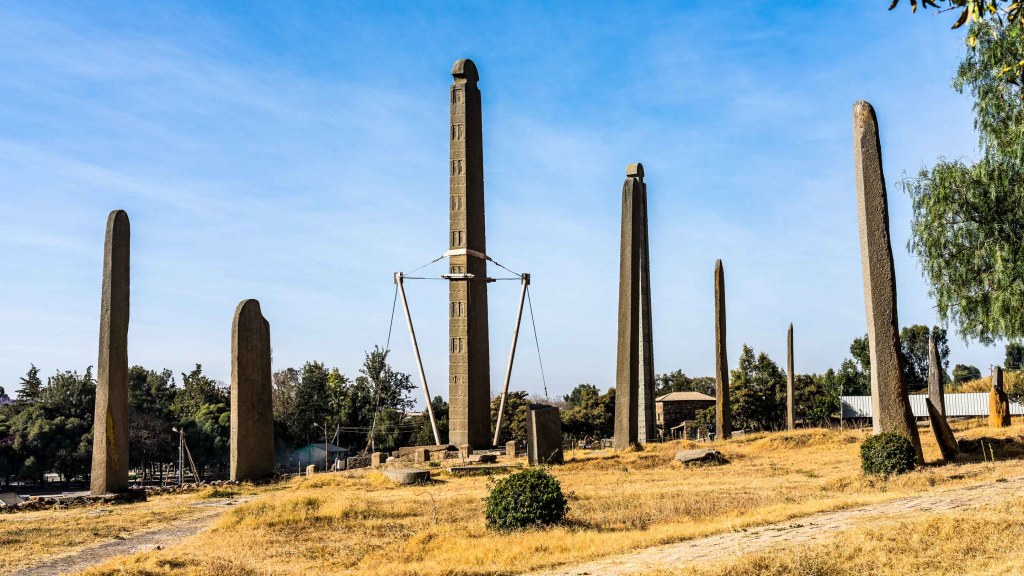

Axum, in today’s Tigray province of Abyssinia (Fake Ethiopia); Axum was the capital of a small kingdom set up in East Africa by the Yemenite tribe Abashat (Hebesha), which was kicked out by the Sabaeans and the Himyarites, namely the major Yemenite kingdoms. Adulis (near today’s Massawa in Eritrea) was the major Abyssinian port of call.

The Horn of Africa, also known as Cape Guardafui or Raas Casiir in Af Somali, was a Ancient Somali harbor renowned to many people all over the world: in the Periplus of the Red Sea, it is called ‘Cape of the Perfumes’ (Akroterion Aromaton). Extensive archaeological excavations have to be undertaken in this location.
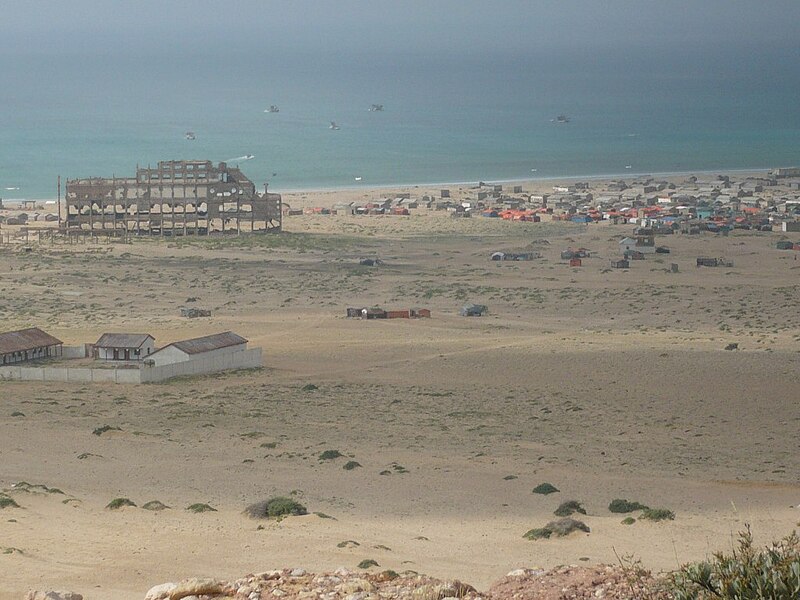

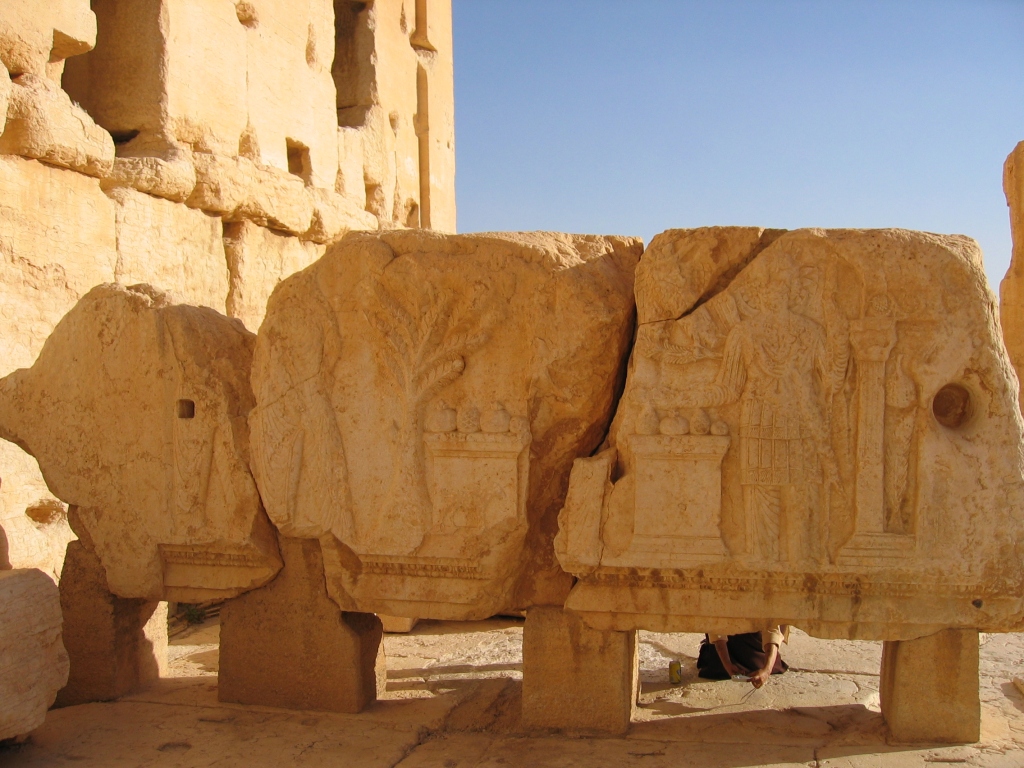
Archaeological excavations have to be undertaken also in Ras (Cape) Hafun (in Af Somali: Ras Xaafuun) further in the South. The remains of the Salt Factory built by the Italians in the early 20th c. are seen on the picture. This site is identified with Opone, another port of call mentioned in the Periplus of the Red Sea. This Ancient Greek name is identical with the Ancient Egyptian name Punt, which denoted an ancient kingdom also known to the Egyptians as Ta-Netjer (the Land of God). Queen Hatshepsut of Egypt organized the most famous (but not the first) Expedition to Punt (around 1475 BCE), dispatching her fleet under Admiral Nehesy (or Nehsi) who conversed with King Perehu and Queen Eti of Punt. The deeds of the historic mission were inscribed in detail on the walls of the second colonnade (southern part) of the mortuary temple of Hatshepsut at Deir al Bahari (Luxor West).

Above:Ras Hafun – Opone/Punt today / Below: Punt before 3500 years

————————————-

Punt 1500 BCE: the Ancient Somalis (Puntites) needed to use ladders to enter their homes

The army of Punt cooperated with the Egyptians for the transportation of the goods of Punt that King Perehu dispatched to Queen Hatshepsut.
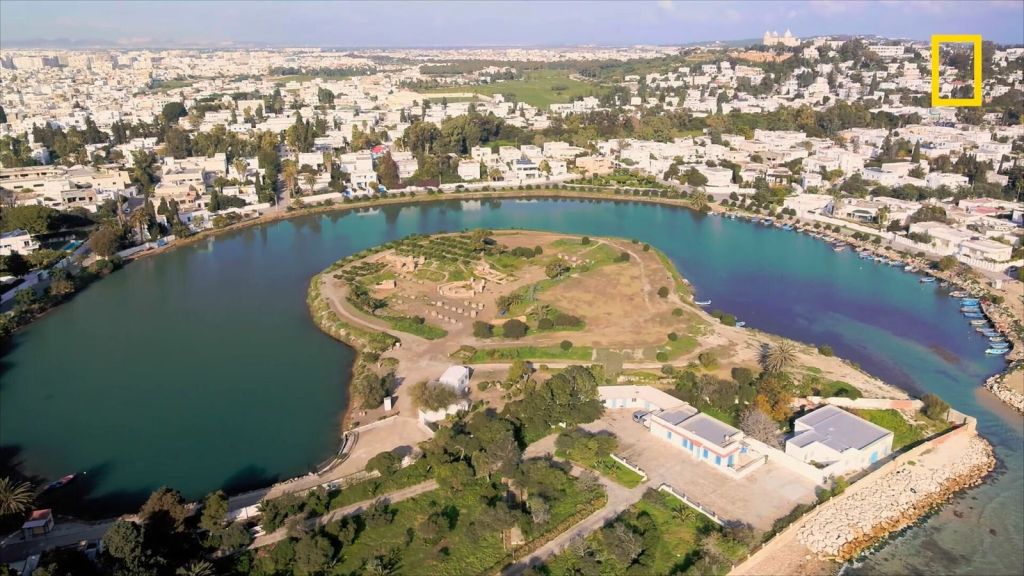

Carthage (Kart Hadasht: ‘New City’): the major Phoenician colony in North Africa became the world’s first maritime empire in the History of Mankind.

—————————————–
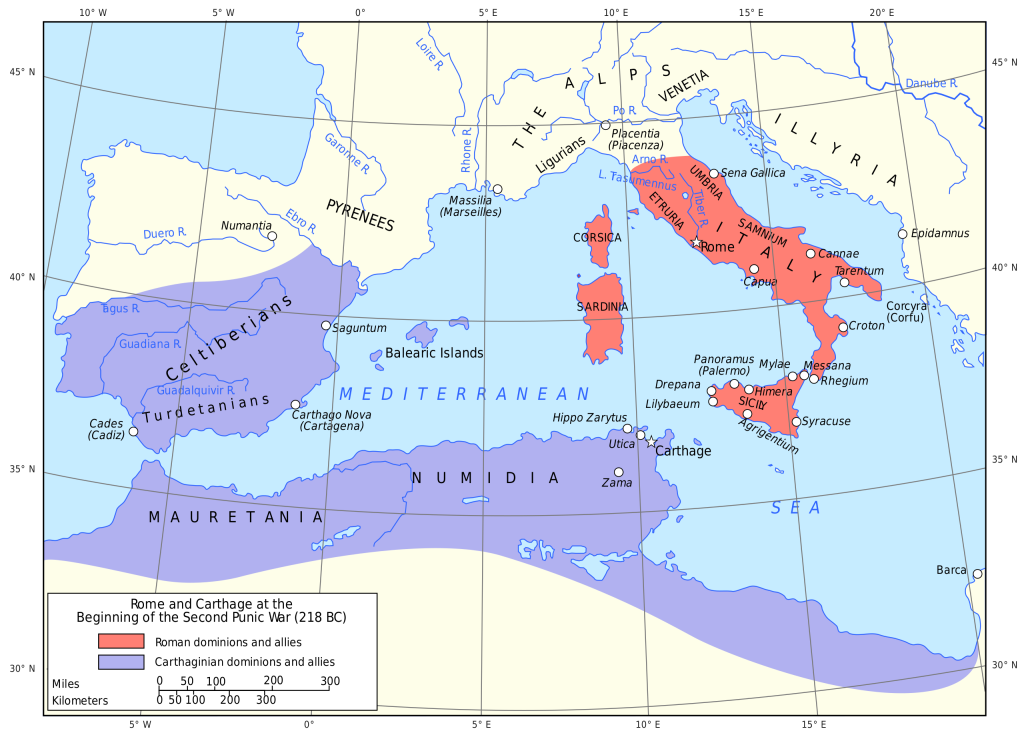
Carthage and the Carthaginian Empire, 218 BCE
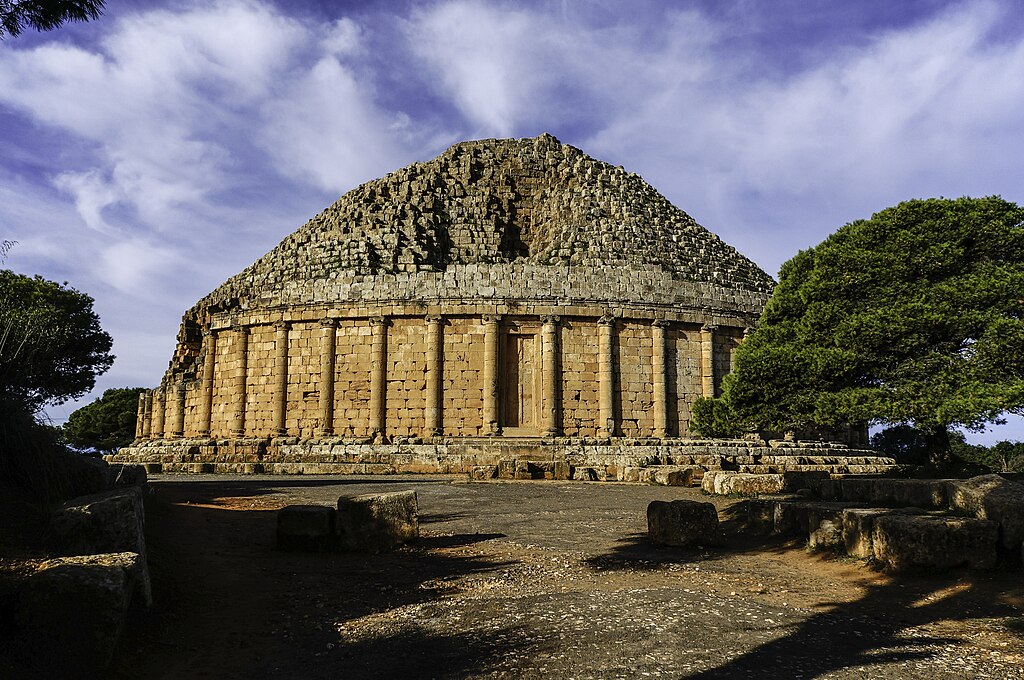

Royal Mausoleum of Mauretania, tomb of Juba II (3 BCE), on the road between Cherchell and Algiers, in Tipaza Province, Algeria
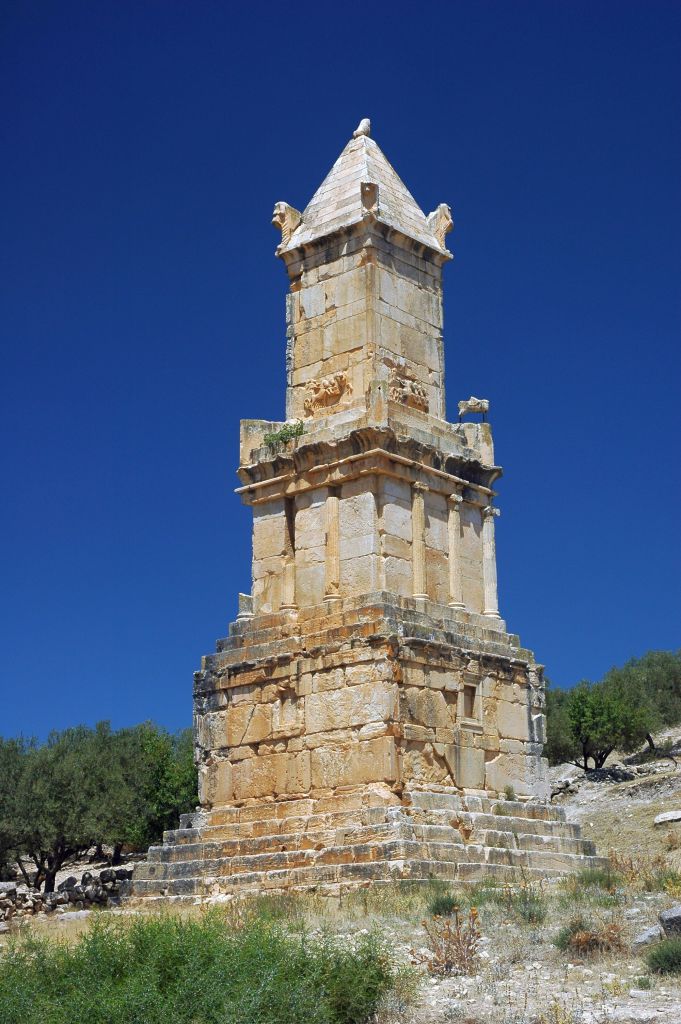

Libyco-Punic Mausoleum in Dougga, Tunisia (2nd c. BCE)
—————————————————————————–
It would not only be a historic investment in terms of National and All-African Education, but it would also constitute a formerly colonized nation’s most radical, resolute and drastic step out of the colonial era. In other words, in 15 (fifteen) years, an effort of such magnitude would bring forth results that would be exponentially greater than what the reputed Institute of African Studies of the University of Ghana achieved in more than 60 years (it was incepted in 1962).
VII. Decolonization means above all De-Anglicization and De-Francization
The previous paragraphs contain a brief criticism of the Afrocentric movement and at the same time reveal why it failed to bring forth substantive results. As a matter of fact, it should have started with an in-depth effort of self-knowledge. Today, in reality, Africans do not know one another, and if they do, this happens at a so superficial level that it is insignificant. This is exactly what I wrote before more than 10 years in a presentation which was widely publicized in Nigeria:
https://www.academia.edu/22843510/AFRICAN_RENAISSANCE_UNIVERSITY_A_VISION
There is no African unity, no African identity, and no African interconnection, when Africans need colonial nations’ languages (English and French) to communicate with one another. In this regard, it is essential at this point to highlight that the current political appearance and the political map of Africa are also of entirely colonial nature; it is what the colonial powers wanted to impose on the Black Continent. That’s why it cannot be taken seriously into account.
Any genuine and integer African cannot accept the colonial falsehood as per which Arabic is the main language throughout North Africa. This ‘happens’ only according to the Orientalist falsehood and due to colonial involvement and interference. In reality, Berber (Amazigh) is the main language throughout North Africa, and all the Africans, who deny this reality, are -quite unfortunately- victims of the colonial powers and of the delusion that European Orientalist and Africanist academics methodically created in order to effectively prevent Africans from achieving true nation building. Then, this implies that there should be Departments of Berber Language and Culture in at least 15 African countries. A Hausa-speaking Nigerian, a Somali, and a Swahili-speaking Kenyan should have the chance (in the perspective of 15 years after the beginning of the herein described educational-academic-intellectual decolonization project in their respective countries) of learning Berber in their high school. Similarly, an Algerian, a Moroccan, a Tunisian or a Libyan should have the chance of learning Hausa, Somali or Swahili in their relevant high schools.
More than 10 million people in Egypt are Copts; for a real African and Afrocentric thinker, the absence of Departments of Coptic Language, Literature and Theology is one of the worst results of the colonial rule throughout Africa. Somalia is an entirely Muslim country; yet, a Department of Coptology would be necessary in Somalia, because only then all the Somalis would understand the historical dependence of the Amhara and Tigray Abyssinians on the Copts, the existing differences between the Amhara and the Copts of Egypt, the pseudo-Christian nature of the Amhara, the reason for which the Christian Orthodox Oromos rejected to have any connection with the Amhara and were (few years ago) directly connected to Copts (the Coptic Patriarchate of Alexandria), and many other similar issues.
To underscore few specific points around which Somali Education, Academic Research, and National Building become one unitary endeavor, I would say the following: if the Amhara tribe and the Abyssinian colonial state proved to be a serious problem and a real threat for Somalia and the Somalis, it is then a national obligation of the Somali government to form a small force of academic specialists, who by studying and learning Coptic language, Coptic cult, Coptic theology, and History of the Coptic Church, will be able to advise correctly on all topics related to the Amhara Abyssinians and to the reason of their hatred of Somalia, Egypt, Islam, and Coptic Christianity. Furthermore, these Somali scholars will be able to unveil to many other Christian Africans the anti-Christian nature of the Amhara and their leaders.
For this to happen, after a first 3 or 4-year curriculum (leading to a B.A.), a Somali graduate should first choose this field as the main objective of his professional academic career; at the same time, he will have to be fully conscious of the fact that his desire to study Coptic in Egypt, specialize in Coptology, and become an expert on the matter does not constitute only his own career choice, but it is also a matter of national importance for Somalia. For this to be confirmed, governmental scholarships will have to be announced and offered for a certain number of years.
A certain perspective has to be given to similar projects leading to the preparation and the launching of a Department of Coptology in Somalia. As I already said at the end of part VI), if we calculate a) the first circle of studies that will lead to a B.A. in Somalia (during which the selection of one or two candidates for specific scholarship for Coptic Studies will take place), b) the postgraduate & doctoral studies (5-7 years) that the Somali graduates will undertake, and c) their return to Somalia in order to launch for the first time a Department of Coptology, it will take ca. 10 years until the state of Somalia establishes a pertinent educational-academic foundation in this regard.
If this is what is needed for the launching of Coptic Studies in Somalia, similar effort has to be deployed for the establishment of many other sectors of Humanities. It will be a matter of Somali students’ commitment and Somali government’s investment in a national and all-African cause.
—————————————————————–
Download the article (text only) in PDF:
Download the article (with pictures and legends) in PDF: