In a previous article published under the title ‘Aristotle as Historical Forgery, the Western World’s Fake History & Rotten Foundations, and Prof. Jin Canrong’s Astute Comments’, I wholeheartedly supported the position taken by the prominent Chinese Prof. Jin Canrong about Aristotle and I explained why Aristotle never existed as he is known today and most of his texts were not written by him, but by the pseudo-Christian Benedictine monks of Western Europe for the purpose of the ferocious imperial and theological battle that Rome carried out against New Rome-Constantinople and the Eastern Roman Empire. You can find the table of contents and a link to the publication at the end of the present article.





Contents
Introduction
I. A fictional concept: the origin of the fraud
II. A construct based on posterior textual sources
III. The deceitful presentation
IV. 5th century BCE texts found in 15th c. CE manuscripts do not make ‘History’.
V. Abundant evidence of lies and deliberate distortions attested in the manuscript transmission
VI. Darius I the Great, the Behistun inscription, and Ctesias
VII. The historical Assyrian Queen Shammuramat and the fictional Queen Semiramis of the ‘Ancient Greek sources’
VIII. The malignant intentions of the Benedictine liars: from the historical Darius I the Great to the fictional Semiramis
IX. The vicious distortions of the Benedictine liars: from Ctesias to Herodotus

Introduction
In the present article, I will offer a typical example of text falsification carried out by the Catholic monks, who did not ‘copy and preserve’ manuscripts of ancient Greek and Latin texts, as it has been mendaciously said by Western European and North American academics and lying scholars, but they purposefully falsified, distorted, concealed, destroyed and/or contrived numerous texts.
This enormous forgery took place in Western Europe between the 2nd half of the 8th century and the 1st half of the 15th century; the colonial era was launched exactly afterwards. For this reason, few manuscripts with Ancient Greek and Roman texts date before the 8th c.; in fact, most of them have been either distorted and replaced or hidden in the vast libraries still owned, controlled and administered that the anti-Christian Roman Catholic Church.
The purpose of this devious and evil effort was the fabrication of a fake narrative about the forged antiquity and the supposed importance of the Western Europeans according to the needs of world conquest, prevalence and preponderance of the pseudo-Christian Roman Catholic Church; this bogus-historical dogma, as direct opposition to and ultimate rejection of Orthodox Christianity, would be initially imposed as the ‘scientific discipline of History’ in Western Europe and subsequently projected onto the rest of the world by means of colonial invasion, indigenous identity destruction, moral integrity demolition, cultural heritage disintegration, educational subordination, economic exploitation, military subjugation, and socio-political domination.
In other words, the monastical scribes and copyists created an entirely fake Euro-centric past, which became the rotten foundation of Western Europe. This fallacy became known as Judeo-Christian world and Greco-Roman civilization. However, the decipherment of ancient languages (Egyptian hieroglyphic, Old Achaemenid Iranian, Assyrian-Babylonian, Sumerian, Hurrian, Hittite, Urartu, Ugaritic, etc) and the study of millions of original texts, which were not copies of earlier sources but contemporaneous to the events that they narrated, sounded the death knell of the era of history fabrication programs.
With the post-Soviet rise of the great continental powers (China, India, Russia, etc.), the economic-military-political-ideological-educational-academic-cultural tyranny of the Western World started being overthrown throughout the earlier colonized world. The historical forgery that the colonial rulers imposed collapsed, the falsehood of the Eurocentric dogma of World History started being revealed and rejected, and an overwhelming project of total de-Westernization appeared as a prerequisite for the liberation of the Mankind from the lies of the European Renaissance, the Western Humanities, the White Supremacism, the Western European colonialism and racism, as well as from the falsehood of numerous subsystems of the construct, such as Classicism, Hellenism, Orientalism, etc.
In our days, it is imperative for anti-colonial scholars to unveil the distortions applied to Ancient Greek and Latin texts by the medieval monks. Consequently, historians from all over the world have to work together in order to denounce and obliterate the Western fraud and the fake History of the Western Man, which consists in arbitrarily taking 14th c. CE manuscripts as authentic narratives of Ancient History.

Jean Adrien Guignet (1816–1854), The Battle at Cunaxa (401 BCE), painting of 1843; typical example of the Western European forgery and of the bogus-historical dogma that European colonials wanted to impose worldwide as ‘History’! The narrative about the Battle at Cunaxa is to be found in Xenophon’s Anabasis; the purported Ancient Athenian author (430-355 BCE) died when Alexander the Great was born, but his text is saved in manuscripts dating back to the period between the 13th the 16th centuries, namely 1600-1900 years after the writer’s death. By selecting themes from the forged Ancient Greek ‘history’, Modern European artists plunged scholars and simple people into a delusion that they call ‘History’. https://medieval.bodleian.ox.ac.uk/catalog/person_89597697
I. A fictional concept: the origin of the fraud
Apparently, the present brief article cannot be an exhaustive presentation of the Western fraud, and of the historical forgery that the Western monks, manuscript copyists, collectors, academics and propagandists attempted to impose worldwide through colonial conquests, massacres and tyrannies. However, I can still enumerate the major founding myths of the Western World.
Two thematic circles of historical distortions and fraudulent claims made by the Western academia revolve around the following two entirely fabricated entities, which have conventionally but erroneously been called
a) “the Greco-Roman world” and
b) “Biblical Israel” and “Judeo-Christian civilization”.
These ahistorical entities never existed. The original concept of those notions is purely fictional, and it therefore remains always unquestioned in the fraudulent Western universities. In this regard, the sources that the Western academics evoke to support their claims are posterior, untrustworthy, forged and therefore worthless.
At times, some of those texts represent merely ancient authors’ misperceptions of earlier texts and authors; however, more often, the ancient texts have been tampered with. On other occasions, ancient texts that refute the lies of other historical sources are hidden from the general public and conventionally discussed among the Western academic accomplices.



Fake terms, nonsensical selection of artworks, intentional use of posterior sources, delusional Modern European paintings and many other techniques were involved in the fabrication of the bogus-historical dogma of the Western World; but how can a Roman relief related to events of the 1st c. CE be taken as relevant of the so-called ‘History of Biblical Israel’, since the Ancient Kingdom of Israel ceased to exist in 722 BCE and the entire population was taken captive to Assyria? All the same, if an author decides to illustrate the topic by means of an Assyrian relief, he surely risks revealing the truth, i.e. the fact that the fake Biblical world was an insignificant periphery of Mesopotamia.

In parallel with the delusion diffused at home and worldwide, the Western academia took good care to produce plenty of sick concepts and laughable notions in their effort to come up with pre-fabricated opponents. Before 100 years, this was done with Hitler and his fake Nazi ideology, which reflected Anglo-Saxon corruption, while being detrimentally opposite to the traditional German culture. Nowadays, fake Muslims are similarly produced by the Western secret services. These pawns, although ignorant, uneducated and idiotic, are foolish enough to portray the so-called Judeo-Christian civilization as the Dajjal, i.e. the Antichrist system, which was prophesied first in Ancient Egypt and in Hittite Anatolia and only much later in Christian and Muslim sources. But the Antichrist system is something real, whereas the Judeo-Christian civilization never existed; it is prefabricated delusion. Those who take it as real will be destroyed.
II. A construct based on posterior textual sources
The entire construct hinges on the deceitful presentation of several types of material forged, collected, concealed, interpreted, contextualized, narrated, repeatedly but intentionally discussed, supposedly questioned, and selectively popularized; this was due to the fact that the said material was incessantly utilized for the colonial needs and targets of the Western European powers (England, France, Holland, Spain, Portugal, and more recently the US). In fact, the Western World’s fake History was created as the ultimate support of all colonial claims.
This process happened within a system in which posterior textual sources (preserved in medieval manuscripts) have occupied the central position, whereas the ancient epigraphic material, which was contemporaneous to the historical events under study, has been deliberately disregarded.
All later discovered data and pieces of information were either adjusted to the construct or methodically hidden; this is how the original concept, pathetically believed almost as a religious dogma, remained totally unchallenged down to our days.
III. The deceitful presentation
The quintessence of the deceitful presentation involves a vicious trick; people (pupils and students, but also scholars and intellectuals, as well as the general public) are taught and made accustomed to care mainly about the absolutely insignificant dates of birth and death of historical persons (authors, rulers, etc.), and not about the dates of the manuscripts in which these individuals are mentioned as supposed authors; this situation turns readers, students and scholars into pathetic idiots.
Subsequently, we cannot seriously afford to describe Herodotus as a 5th c. BCE writer, because there is no manuscript with texts attributed to him, dating before the 10th c. CE. In addition, if we take into account the enormous number of other ancient authors decrying, denigrating and rejecting Herodotus’ absurdities and malignancy, we have to permanently and irrevocably obliterate Herodotus from the History of Mankind and consider his false, paranoid and racist texts as a double Crime against the Mankind:
first, with respect to the original narrative (to which we don’t have access as it was distorted by medieval monastical scribes and copyists) because the author attempted to disparage the superior Iranian civilization and the majestic Achaemenid universalist empire, while undeservedly praising the South Balkan barbarians, and
second, as regards the currently available text, which was forged as per the discriminatory intentions of the monks who altered and distorted it in their effort to fabricate the fake, modern divide (or dichotomy) East-West, and to offer a shred of historicity to it.
IV. 5th century BCE texts found in 15th c. CE manuscripts do not make ‘History’.
People get therefore addicted to considering as a true and original ‘work’ (of an ancient author) the manuscript (or manuscripts) in which the specific treatise, essay or book was copied perhaps 10 or 15 centuries after the author composed it. Due to a long chain of intermediaries (namely library copyists, librarians, scholars, monks, collectors, purchasers and/or statesmen), the transmitted text may have been partly or totally changed.
There is absolutely no guarantee as regards the honesty, the good intentions, the unbiased attitude, and the benevolent character of the perhaps 5, 10, 20 or 50 persons who -living in different eras and without knowing one another- may have constituted the chain of (unknown to us) intermediaries between the hand of the author and that of the last copyist whose manuscript was preserved down to our times.
Example: very little matters today whether the ancient author Diodorus Siculus or Siceliotes (西西里的狄奧多羅斯) actually lived in the 1st c. BCE or in the 3rd c. CE; quite contrarily, what is important for history-writing is the fact that the earliest known manuscript of his famous ‘Bibliotheca Historica’ (世界史) dates back to the 10th c. CE.
Consequently, the first piece of information that should be stated after the name of any ‘ancient’ Anatolian, Macedonian, Thracian, Greek, Roman and other author is the date of the earliest extant manuscript of his works.

V. Abundant evidence of lies and deliberate distortions attested in the manuscript transmission
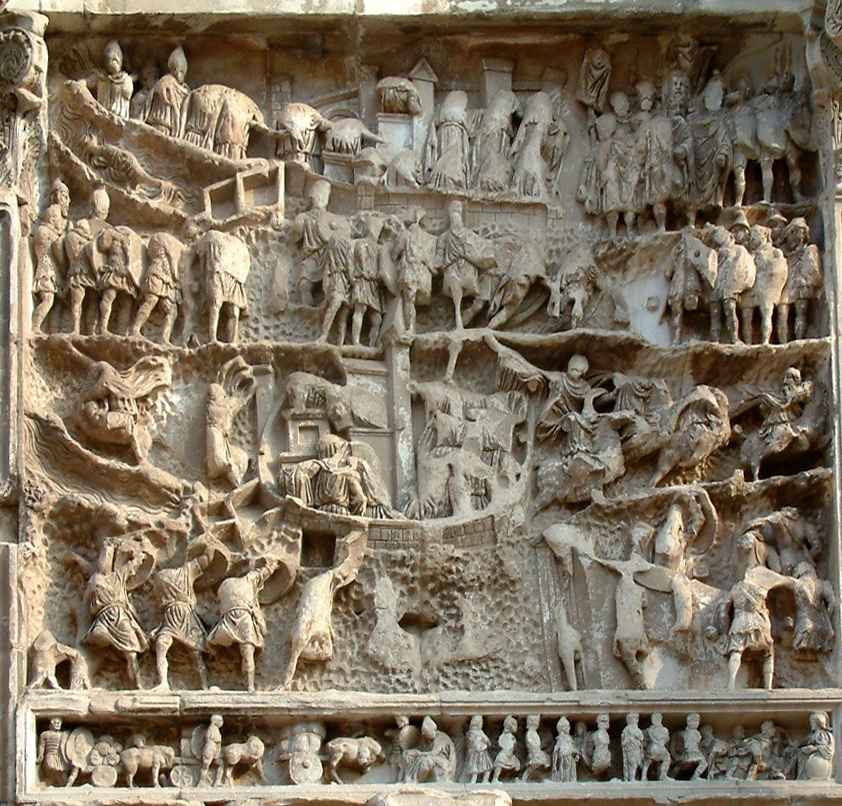
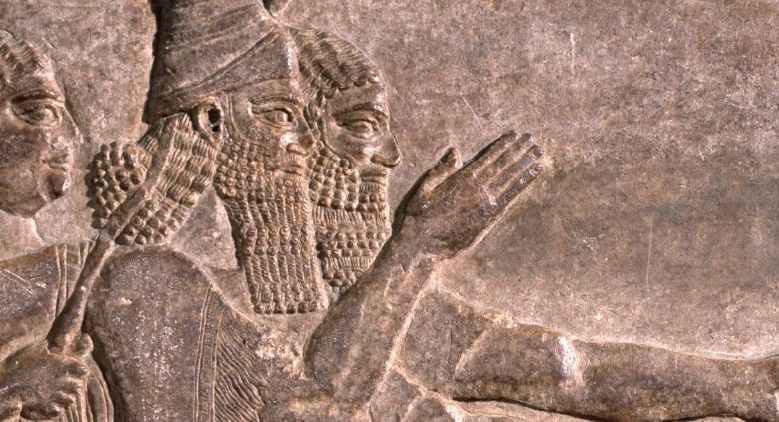
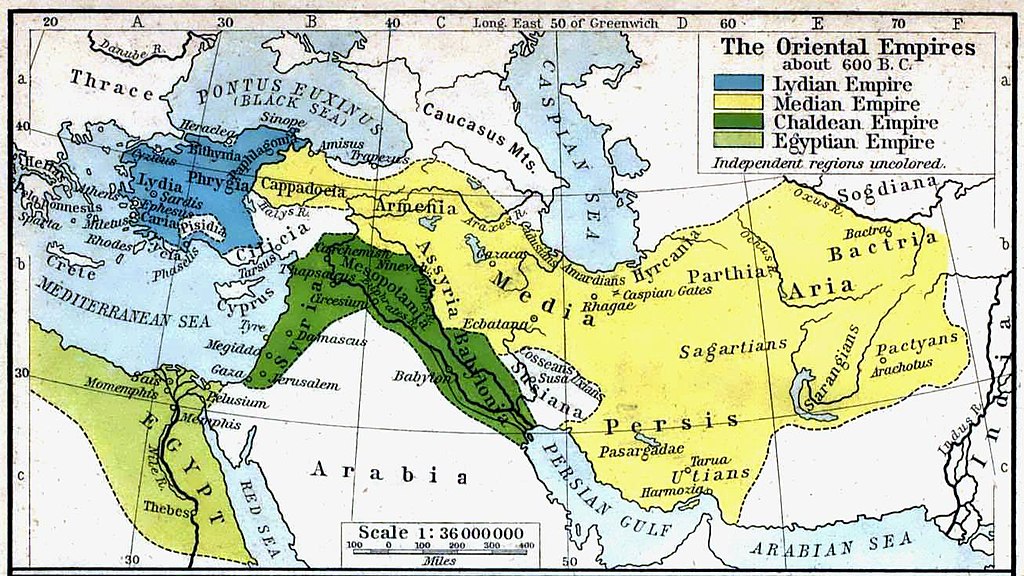
An extraordinarily high number of original sources excavated in Mesopotamia, Egypt, Anatolia, Canaan, Iran and elsewhere, and subsequently deciphered, can be dated with accuracy; example: the Annals of great Assyrian emperor Tiglath-pileser III (745-727 BCE) were written during his reign. They are contemporaneous and therefore original.

Part of the Annals of the Assyrian Emperor Tiglath-pileser III (745-727 BCE) that were written and depicted on the walls of imperial palace at Kalhu (modern Nimrud, in Northern Iraq): representation of the Assyrian campaign against Babylonia in 728 BCE; contrarily to the Ancient Greek sources, which were hypothetically preserved in manuscripts written 1500 years after the supposed author elaborated his narrative, the Assyrian texts are trustworthy and valuable sources of information, because they were formulated at the same time as the events therein narrated. But not one Ancient Greek relief or text was found to be contemporaneous with Herodotus’ fictional battle of Thermopylae.
However, in striking contrast to them, almost all the manuscripts with the works of ancient Greek and Roman authors whose texts have formed the backbone of the fraudulent historical dogma of the Western academia are not contemporaneous but posterior by, at times, 1500 or 2000 years.
Even worse, numerous ancient Greek authors’ texts were not preserved through a manuscript tradition at all; they were saved as references in posterior authors’ works. This concerns, for instance, Ctesias (克特西亞斯), an Ancient Carian (Anatolian) physician and erudite scholar, who lived and worked in the court of the Achaemenid Iranian emperor Artaxerxes II in the 5th c. BCE.
Later, willing to offer potential guidebooks to Iran and India for the use of various peripheral peoples and tribes of the Balkan region, Ctesias elaborated in Ancient Ionian (愛奧尼亞希臘語) two treatises to describe the state of things in Iran and in India. To the Western academic bibliography, his works are known (in Latin) as ‘Persica’ and ‘Indica’.
These texts were not saved integrally in manuscripts copied for the purpose of preserving Ctesias’ works, but they were preserved in Diodorus Siculus’ ‘Bibliotheca Historica’. Although he is not known through authentic and contemporaneous Iranian sources, we can deduce that Ctesias certainly spoke fluently the official language of the Empire and read Old Achaemenid cuneiform. Eventually, he may have also studied and learned Babylonian and Elamite cuneiform, namely two ancient Mesopotamian cuneiform languages and writings the use of which was maintained by Iranian scribes.
Apparently, Ctesias had a firsthand insight, as he lived for many years in Parsa (Persepolis), the capital of the Achaemenid Empire and he also traveled extensively along with the Iranian emperor. But, unfortunately, the following ordeal was produced.


VI. Darius I the Great, the Behistun inscription, and Ctesias
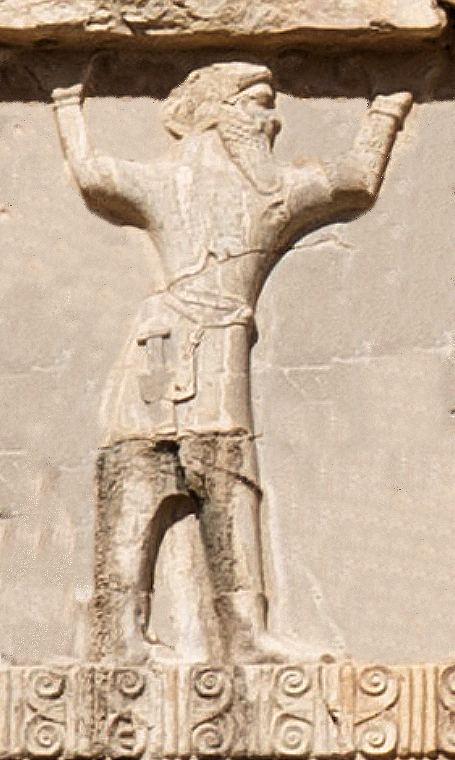
One century before Ctesias served Artaxerxes II, the empire of Iran was saved by Darius I the Great (大流士一世; reign: 522-486), who overthrew a usurper, namely the Mithraic (密特拉教祭司) magus Gaumata (高墨达), and by so doing, preserved on the throne a dynasty of faithful Zoroastrian (瑣羅亞斯德教徒) monarchs.
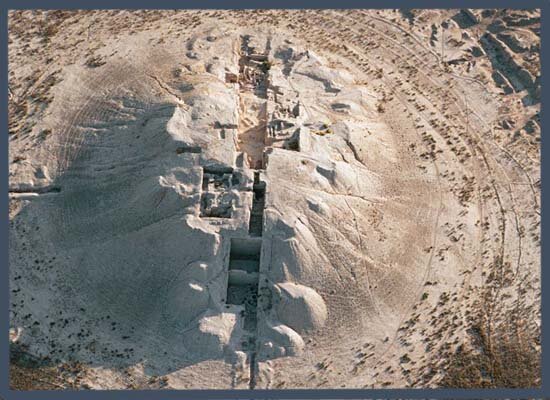
To commemorate his great victory and the consolidation of the his dynasty, Darius I the Great had an enormous rock relief and a monumental inscription (貝希斯敦銘文) engraved on the rocks of Mount Behistun (貝希斯頓山), at a distance of 150 km west of Hamadan (哈马丹; Ekbatana/埃克巴坦那) in Western Iran (15 m high by 25 m wide and 100 m up the cliff). As it can be easily understood, these events occurred after the assassination of Cambyses, at the very beginning of Darius I the Great’s reign.
It goes without saying that the successors of Darius I the Great and the imperial Iranian administration knew perfectly well the historical details and were fully aware of the imperial inscription that immortalized the event, which had obviously become the cornerstone of the imperial education.

Mount Bisotun (rather known as Behistun in Western bibliography)




The Behistun inscription

Representation of the Achaemenid Iranian Emperor Darius I the Great in the Behistun inscription; he is trampling the defeated Gaumata.

Behistun relief of the defeated Elamite ššina rebel

In the vast Achaemenid Iranian Empire, Imperial Aramaic was the lingua franca in which people from different provinces (satrapies) used to communicate; numerous official documents were translated from cuneiform to alphabetic writing and sent to the various administrators (satraps). The Behistun papyrus from the Elephantine Island (in Aswan, Upper Egypt) contains an Imperial Aramaic translation of the Inscription of Behistun; excavated in 1906-1908 by the German Orientalist Eduard Sachau and published in 1911, the text is known as DB Aram and as TADAE C2.1+3.13. About: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Behistun_papyrus https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Behistun_Inscription https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Textbook_of_Aramaic_Documents_from_Ancient_Egypt
VII. The historical Assyrian Queen Shammuramat and the fictional Queen Semiramis of the ‘Ancient Greek sources’
However, one century later, when Ctesias lived in Iran, served the Iranian Emperor, and spoke Old Achaemenid Iranian (and if not, he was surrounded by the Empire’s top interpreters and advisers), something disastrously odd ‘happened’.
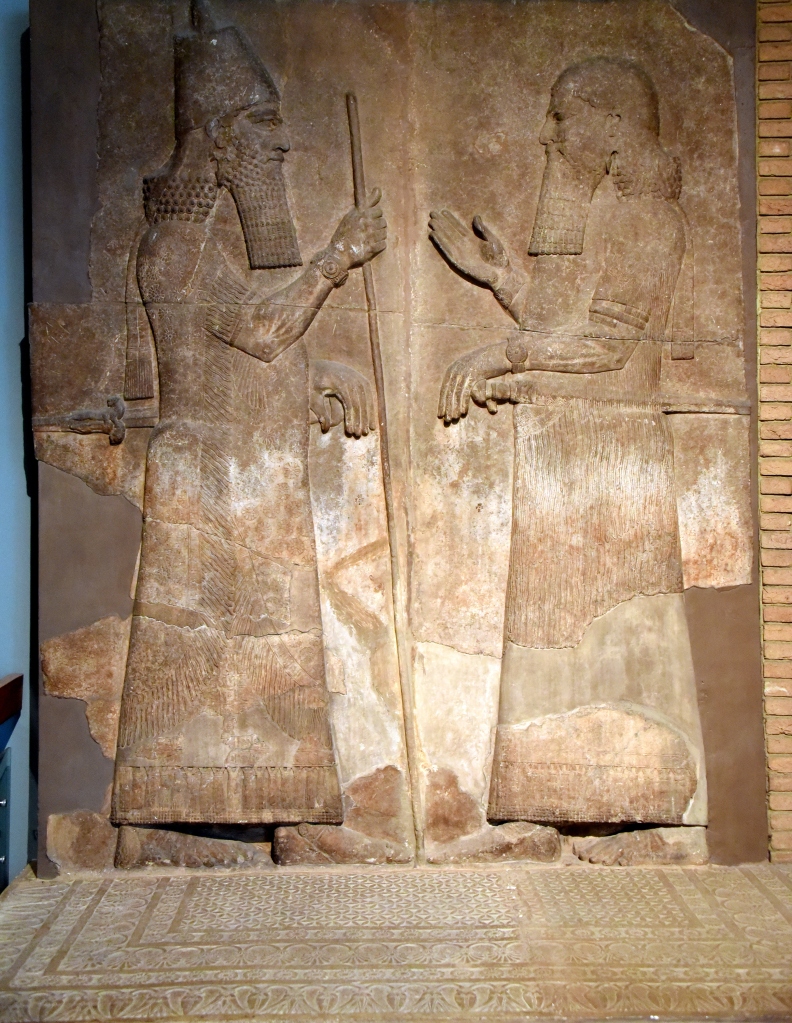
According to Diodorus Siculus, who explicitly stated that he extensively quoted from Ctesias’ text (Bibliotheca Historica, II 13), the imperial Carian physician and author appears to have attributed the Behistun inscription and the rock reliefs to none else than the Assyrian Queen Shammuramat (薩穆-拉瑪特), who was the queen consort of the Assyrian Emperor Shamshi Adad V (沙姆什·阿達德五世; reign: 824-811) and co-regent (811-805) during the first years of reign of her son Adad Nirari III (阿达德尼拉里三世; reign: 811-783)!

(Above:) stela of Shamshi-Adad V from the Nabu Temple at Kalhu/Nimrud; (below:) stela of Adad Nirari III from Tell al Rimush (also known as the ‘Mosul marble stele’)


(Above:) the stela of Shammuramat from the city of Assyria (Ashur); the great queen and queen mother is described as the wife of Shamshi-Adad V, the mother of Adad-Nirari III, and the daughter-in-law of Shalmaneser III (actually in the Pergamon Museum, Berlin, Germany); (below:) detail


Actually in the Maraş (Germanikeia/Kahramanmaraş) Archaeology Museum, the Pazarcık Stele was found in Kizkapanli, near the Pazarcik village, ca. 30 km SE of Maraş in Turkey; the monument was a boundary stele constructed by the Assyrian Emperor Adad-nirari III in 805 BCE. It demarcated the borders between Assyria and the Neo-Hittite kingdoms of Kummuh (later known as Commagene) and Gurgum. The queen mother Shammuramat is mentioned as taking part in the military campaigns undertaken by the Assyrian Emperor in the region.
Furthermore, in the ‘Ancient Greek’ text of Diodorus Siculus, the monumental inscription was said to be written in Assyrian cuneiform (Συρίοις γράμμασιν)! Even worse, in the same text (as preserved today), it was also stated that, in the rock relief, there was also a representation of the Assyrian queen!
Ctesias’ text, as preserved by Diodorus Siculus, is truly abundant in information, but it is historically impossible and therefore entirely forged. Due to this and many other texts, an enormous chasm was unnecessarily formed between
a) the historical queen Shammuramat of Assyria, whose historicity is firmly undeniable, due to the existence of several contemporaneous cuneiform sources excavated in Assyria, and subsequently deciphered and published,
and
b) the purely fictional Assyrian queen Semiramis (沙米拉姆) of the posterior Ancient Greek textual sources that were supposedly ‘preserved’ (but in reality deliberately distorted and forged) in the Benedictine manuscripts of Western Europe’s monasteries.

The fictional Semiramis of Western Europe: ‘Semiramis receiving news of the rebellion in Babylon’, painting by Giovanni Francesco Barbieri (also known as Il Guercino; 1591-1666), 1624 (Oil on canvas, currently in the Museum of Fine Arts, Boston)

Semiramis called to Arms, by Alessandro Leone Varotari (also known as Il Padovanino; 1588’1649)

Semiramis Building Babylon (1861) by Edgar Degas
However, if we examine closely the facts, we will surely understand what truly occurred in this case; then, we will be able to fathom how the fake History of the Western world was fabricated.
The Behistun inscription is trilingual, as it was written in Old Achaemenid Iranian (the earliest form of written Iranian languages), Babylonian, and Elamite; this was a very common practice during the Achaemenid times (550-330 BCE). The main figure of the associated rock relief is Darius I the Great, evidently the representation of a male royal.
One way or another, with respect to the Behistun inscription and rock relief, Ctesias certainly knew everything that we know today after the successive decipherments of the Old Achaemenid, Babylonian and Elamite cuneiform writings, or perhaps even more, due to the then extant oral tradition.
VIII. The malignant intentions of the Benedictine liars: from the historical Darius I the Great to the fictional Semiramis
The Behistun inscription is not Assyrian; the representation is not that of female royal; and the monument is totally unrelated to Shammuramat, who had lived 300 years before Darius I the Great and 400 years before Artaxerxes II’s physician Ctesias. More importantly, by that time, the Assyrian Empire did not occupy the lands surrounding Behistun. Accompanied by Iranian imperial officers and his associates, Ctesias certainly learned all the details of the monumental inscription that we can now read in articles, courses, lectures, books and encyclopedias.
The narrative was a triumph for Darius I the Great and a spectacular rebuttal of the vicious Mithraic Magi who had supported the defeated evil sorcerer and villain Gaumata. Apparently, writing a guidebook for Iran to help marginal people of the Empire’s Balkan periphery, Ctesias did not have any reason to say lies. Moreover, we don’t have any reason to believe that Diodorus Siculus needed to distort the truth to that extent, when copying and thus preserving Ctesias’ masterpiece for the posterity.
However, the transmission of the details about the Behistun inscription embarrassed the Benedictine copyists who wanted to denigrate Darius I the Great and to portray his great empire in a most derogatory manner. They had already proceeded in this manner, distorting other manuscripts, forging texts, and fabricating their pseudo-historical narratives at will.
That is why Ctesias’ pertinent text, which had certainly been preserved in its original form within Diodorus Siculus’ Bibliotheca Historica, was intentionally distorted by the Benedictine ‘Holy Inquisition of Libraries’, which fabricated the myths of today’s Western world some time after the middle of the 8th c. CE. To be accurate, Ctesias’ historical description was entirely replaced by a fictional and historically nonsensical account.
The unbelievable lies -invented and included in Diodorus Siculus’ quotations from Ctesias- risked making of the fictional queen Semiramis a world ruler! Whereas the Assyrian Empire at the end of the 9th c. BCE did not control even the western half of today’s Iranian territory, the unequivocally mythicized Semiramis had supposedly sent her armies up to India where those fictitious Assyrian soldiers were trampled by the elephants. This worthless narrative that replaced Ctesias’ original text may very well have been invented as a ‘historical’ excuse for Alexander the Great’s failure to advance deep inside India.

The fictional Semiramis of Modern Europeans: she condemns her husband Ninus to death; painting by Nicolaus Knüpfer (1609-1655), created after 1622. Currently in the Museum of Fine Arts, Budapest.
IX. The vicious distortions of the Benedictine liars: from Ctesias to Herodotus
But if the fictional Semiramis’ Indian campaign is entirely false, so are then the preposterous narratives of Herodotus about Darius I the Great’s and Xerxes I the Great’s campaigns in the insignificant and barbarian circumference of South Balkans. These texts involved evil purposes, heinous anti-Iranian biases, fictional battles, racist discourses, vicious lies, incredibly large number of the Iranian armies, and absurdly high number of Iranian casualties.
The mendacious but idiotic Benedictine monks, who wrote those slander tales did not apparently expect that, sometime in the future, excavations would bring to light splendid Iranian antiquities, original cuneiform documentation, and trustworthy contemporaneous historical sources, whereas a systematic effort of decipherment would offer to people all over the world direct access to historical texts written in dead languages, thus irrevocably canceling Herodotus’ nonsensical report and, even more importantly, the later distortions that the Benedictine monks made on their worthless manuscripts.
In any case, had those fictional campaigns against ‘Greece’ had a shred of truth to them, they would have certainly been documented one way or another in various Old Achaemenid, Babylonian, Elamite, Imperial Aramaic, Egyptian hieroglyphic or other sources; but they were not.
Even worse, the meaningless and ludicrous battles of Marathon, Thermopylae, Salamis, and their likes would have been commemorated by the Seleucids, the Ptolemies, and the Attalids all the way down to the Romans and the Eastern Romans. But we know quite well that the nonexistent, fictional past of the so-called Ancient Greek world was absolutely irrelevant to them: precisely because it had not yet been fabricated.
===================
Aristotle as Historical Forgery, the Western World’s Fake History & Rotten Foundations, and Prof. Jin Canrong’s Astute Comments
Contents
I. Aristotle: a Major Founding Myth of the Western World
II. When, where and by whom was the Myth of Aristotle fabricated?
III. The Myth of Aristotle and its first Byproducts: Scholasticism, East-West Schism, the Crusades & the Sack of Constantinople (1204)
IV. Aristotelization: First Stage of the Westernization and the Colonization of the World
V. Aristotelization as Foundation of all the Western Forgeries: the so-called Judeo-Christian Heritage and the Fraud of Greco-Roman Civilization
VI. The Modern Western World as Disruption of History
VII. The Myth of Aristotle and the Monstrosity of Western Colonialism
—————————————-
Download the article (text only) in PDF:
Download the article (text and pictures with legends) in PDF: