Pre-publication of chapter IX of my forthcoming book “Turkey is Iran and Iran is Turkey – 2500 Years of indivisible Turanian – Iranian Civilization distorted and estranged by Anglo-French Orientalists”; chapters VI, VII, VIII, IX and X form Part Three (Turkey and Iran beyond Politics and Geopolitics: Rejection of the Orientalist, Turcologist and Iranologist Fallacies about Achaemenid History) of the book, which is made of 12 parts and 33 chapters. Chapters VIII and X have already been pre-published.
Until now, 19 chapters have been uploaded as partly pre-publication of the present book; this chapter is therefore the 20th (out of 33) to be uploaded. At the end of the text, the entire Table of Contents is made available. Pre-published chapters are marked in blue color, and the present chapter is highlighted in gray color.
In addition, a list of all the already pre-published chapters (with the related links) is made available at the very end, after the Table of Contents.
The book is written for the general readership with the intention to briefly highlight numerous distortions made by the racist, colonial academics of Western Europe and North America only with the help of absurd conceptualization and preposterous contextualization.
———————–

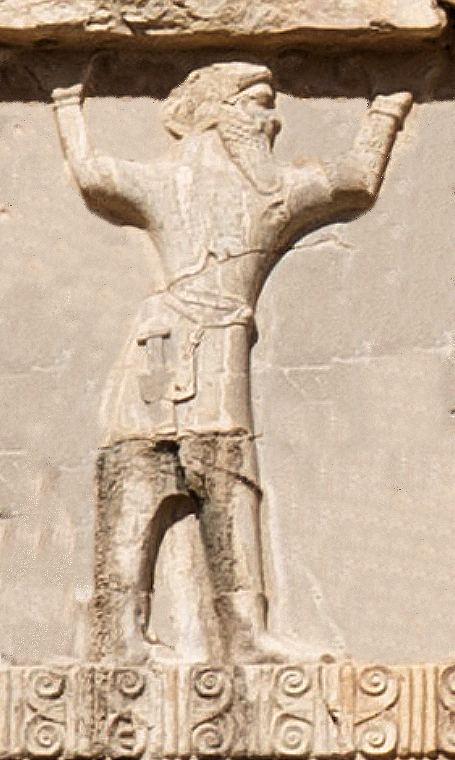
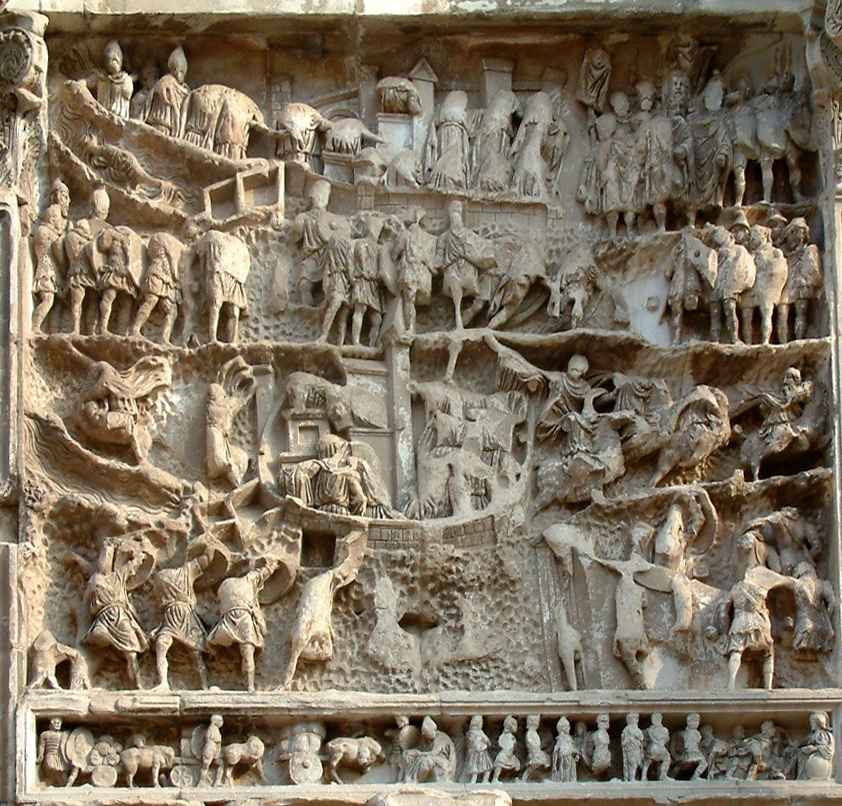
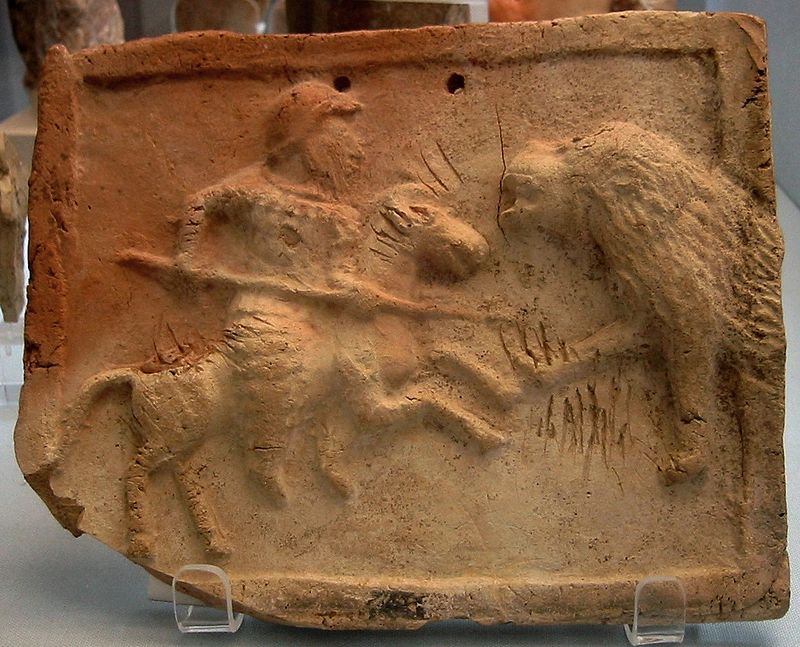
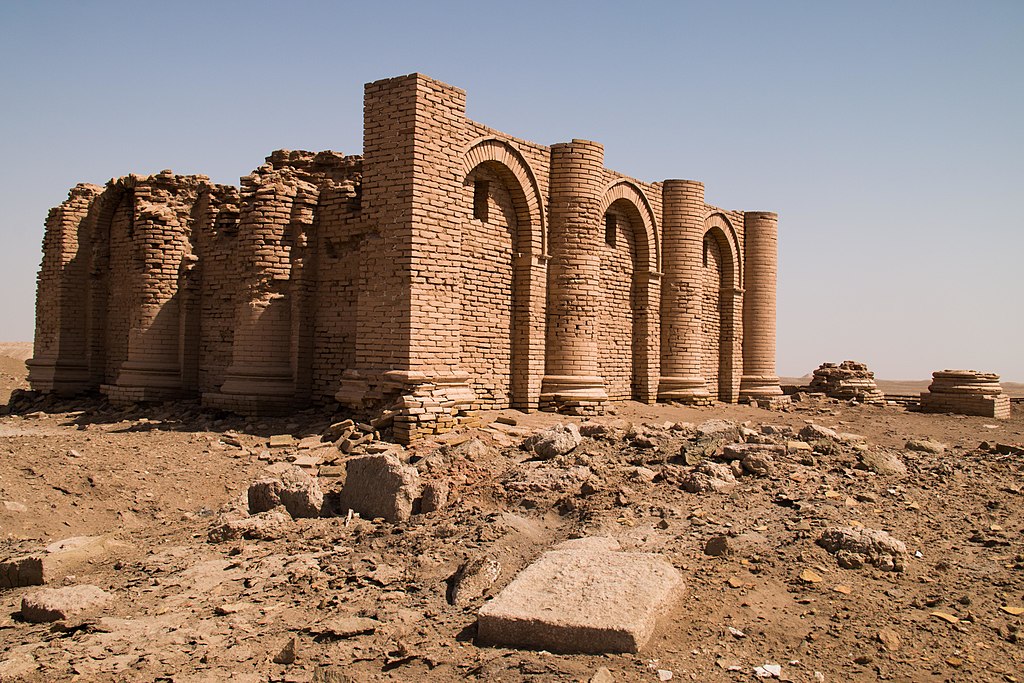
The nations of the Achaemenid Empire as depicted on the façade of the tomb of Darius I the Great in Naqsh-e Rustam, 7 km from Persepolis.
The reality of the multi-national, multi-lingual, multi-religious, multi-cultural Empire of the Achaemenid dynasty is simple to grasp, if we eliminate colonial Orientalist fallacy: in the immense periphery, many diverse historical nations, like the Scythians of Ukraine, the Ionians and the Lydians of Western Anatolia, the Egyptians, the Phoenicians, the Aramaeans, the Babylonians, and the Indians of the Indus Delta region, constituted vital parts and key elements of the Iranian Empire.
Contrarily, in the central parts of the vast empire, the various nations that settled and lived there were not culturally and historically diverse, but rather homogeneous; due to tribal interconnections and clan affiliations, an extensive multilingualism existed among them, being greatly impacted by sedentarization, semi-nomadism, and labor division processes. These populations, irrespective of their place of origin, once they became sedentary, focused on agriculture, craftsmanship, and local administration; on the other hand, the nomadic and semi-nomadic groups made brave, experienced soldiers, excelled in cattle-keeping and practiced trade.
That is why their original languages developed differently, adapting syntax and usage to the very different needs of the speakers’ lives; the soldiers spoke Turanian dialects and the sedentary populations expressed themselves in Iranian dialects, which were both in their process of formation. In the vast borderless land that stretches from NE Siberia to Central Asia to the Iranian plateau and to Eastern Europe, an interminable interconnection generated the conditions of life that 1500 after the first Achaemenid Shahs Ferdowsi narrated with outstanding clarity: Iran and Turan have always been an indivisible entity whereby
a) the soldier, the semi-nomad, and the mystic speaks Turanian idioms, and
b) the administrative employee, the sedentary, and the priest uses Iranian vernaculars.
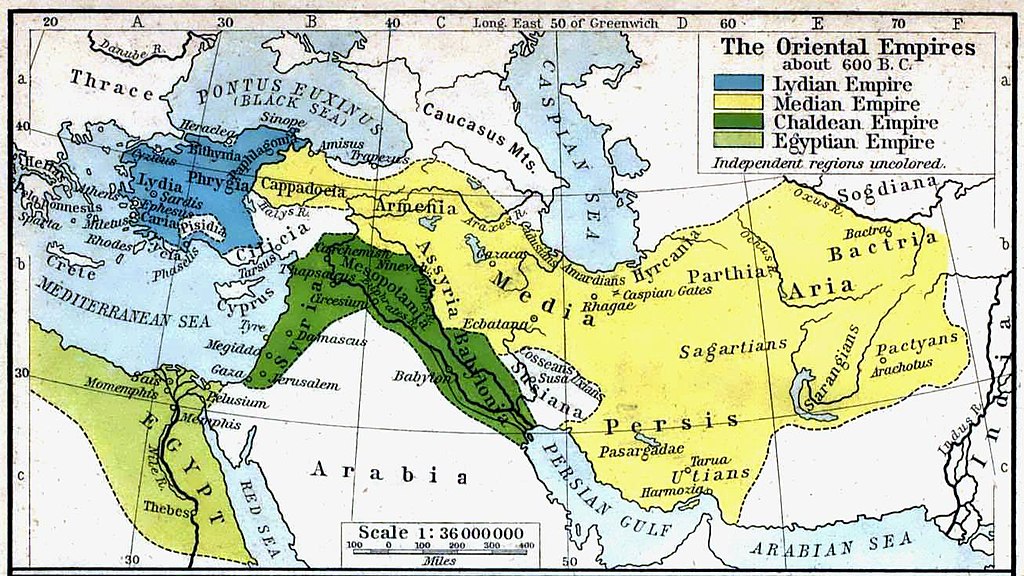
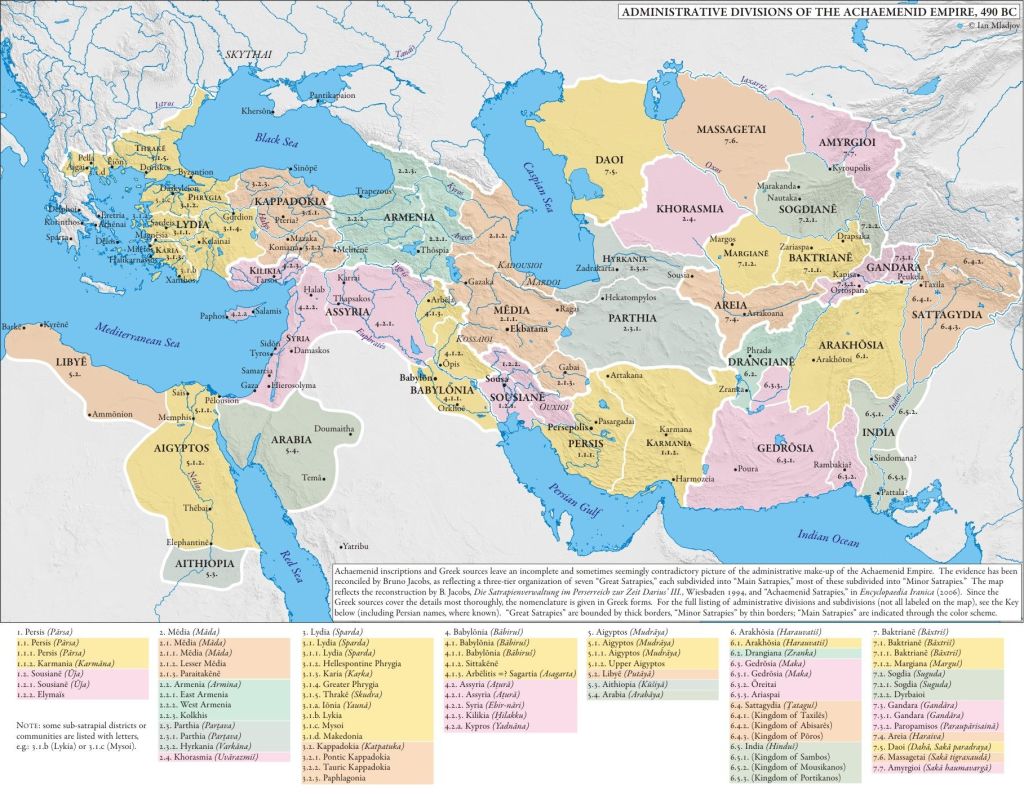
The central part of the Achaemenid Empire stretched over the territory of modern states of Iran, Azerbaijan, Armenia, Georgia, Turkmenistan, Uzbekistan, Tajikistan, Kyrgyzstan, Afghanistan, and Pakistan.
If we refer to names of Achaemenid satrapies, Iran’s central parts were: Mada (Media and Media Atropatene), Parthava (Parthia), Asagarta (Sagartians), Parsa (Persia), Karmana (Carmania), Maka (Gedrosia), Zranka (Drangiana), Harauvatish (Arachosia), Thatagush (Sattagydia: downstream Indus), Hindush (Punjab: Pentapotamia), Gandara (Paropamisos: North Pakistan), Baxtrish (Bactria), Haraiva (Areia: NW Afghanistan & NE Iran), Suguda (Sogdiana), Margush (Margiane), Varkana (Hyrcania), Daha and Uvarazmish (Chorasmia). These nations are portrayed by colonial Orientalists as all entirely related to Persians. This is a lie that originates from the fallacious colonial equation “Fars equals Iran”. About:
https://www.academia.edu/43365931/Iran_is_not_Persia_and_Persia_is_not_Iran
Greater ethno-linguistic affinities with Turanian (Turkic) nations seem to have had the following central Iranian nations: Atropatene, Parthia, Hyrcania, Daha and Chorasmia. In reality, the central parts of the Iranian Empire were inhabited by both Iranian and Turanian nations that had evidently greater cultural affinities among themselves than with other nations of the Iranian periphery and expansion.
Of all these nations, the two most important for the imperial elite were the Ancient Azeris (Atropatene) and the Ancient Persians (Fars / Persia). The latter held the royal power and administration, whereas the former were the vicars of Zoroastrian Orthodoxy. However, the most determinant trait of the Achaemenid royalty was absolute devotion and unquestionable submission to Zoroaster’s monotheistic faith. That is why the Achaemenid court was always adamant against the Mithraic Magi and the Iranian emperors reprimanded in the most resolute manner the polytheistic Mithraists’ efforts to either alter the original meaning of the Zoroastrian monotheism or to usurp the throne and then impose a counterfeit, fake shah who would be the worthless puppet of the villainous Magi.

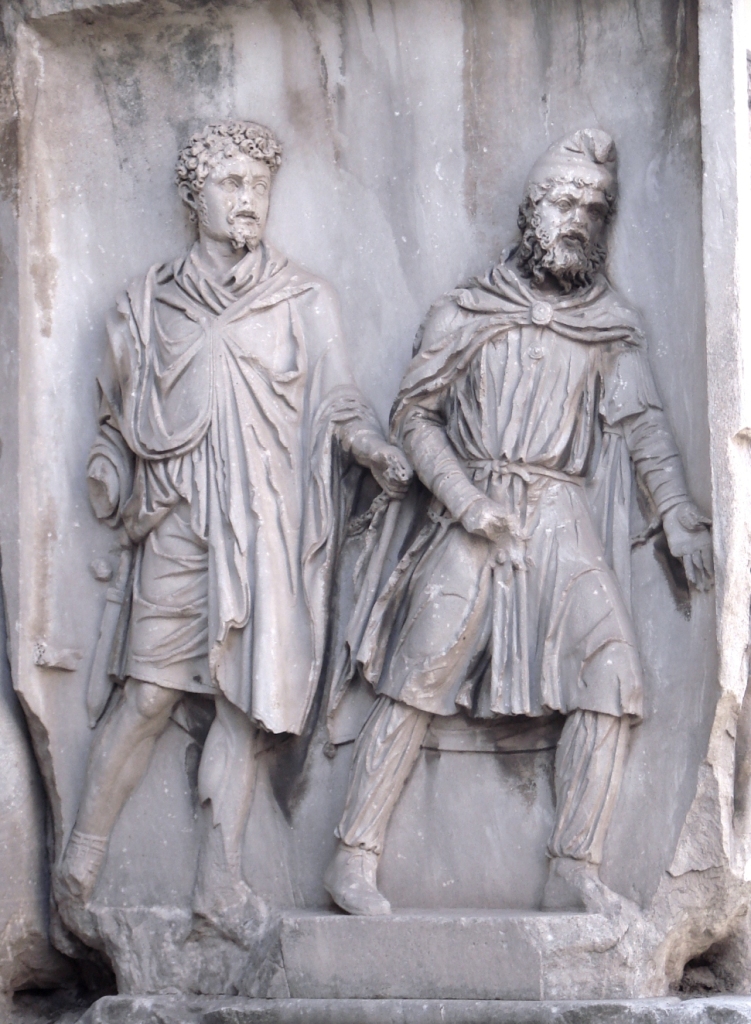
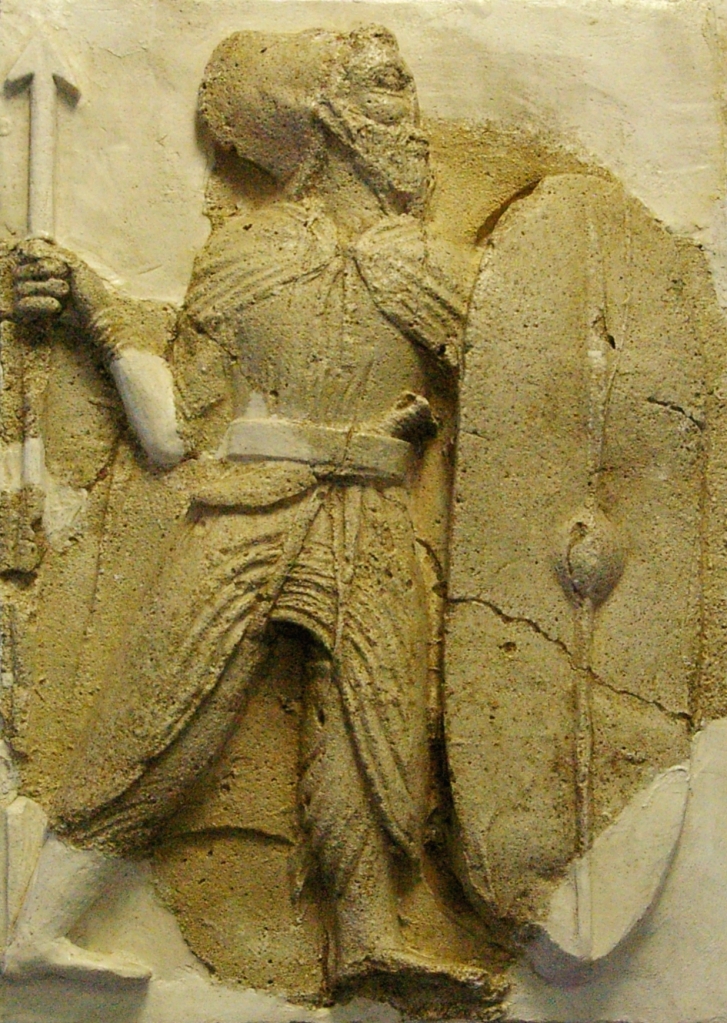
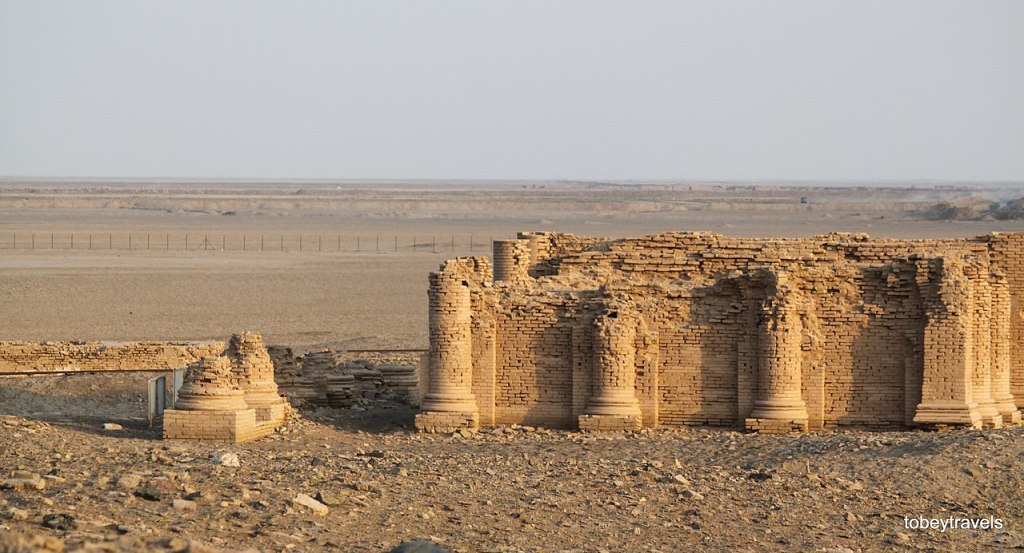
The nations of the Achaemenid Empire as depicted on the façade of the tomb of Xerxes I the Great in Naqsh-e Rustam, 7 km from Persepolis.

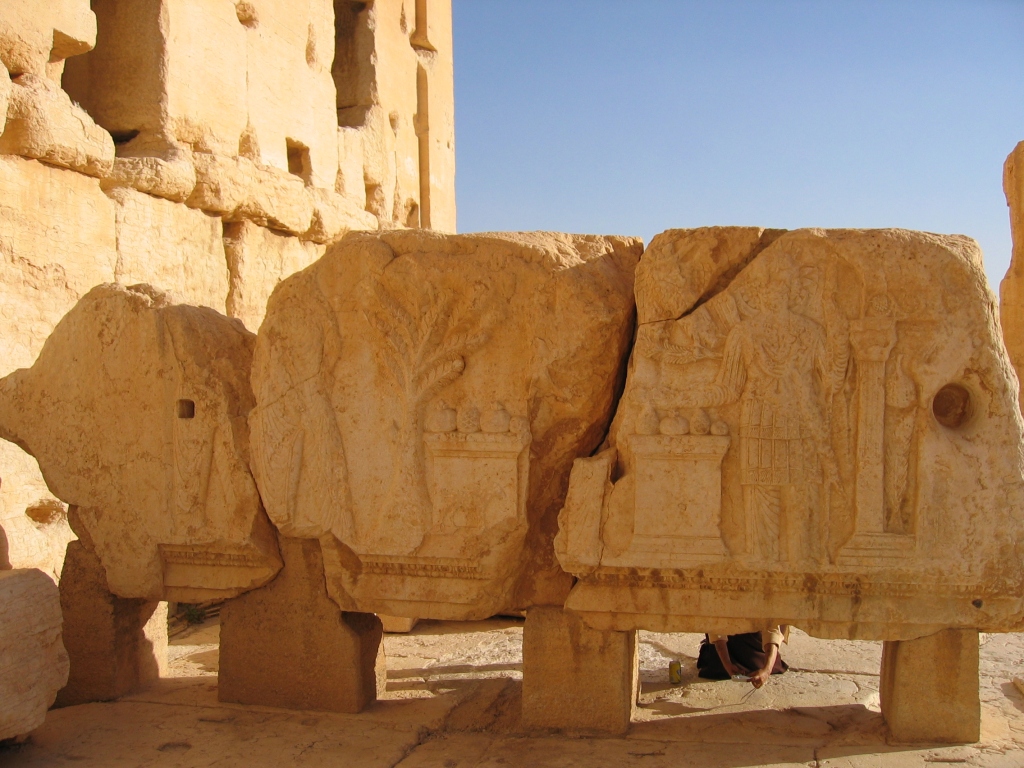
The nations of the Achaemenid Empire as depicted on the façade of the tomb of Artaxerxes I in Persepolis.
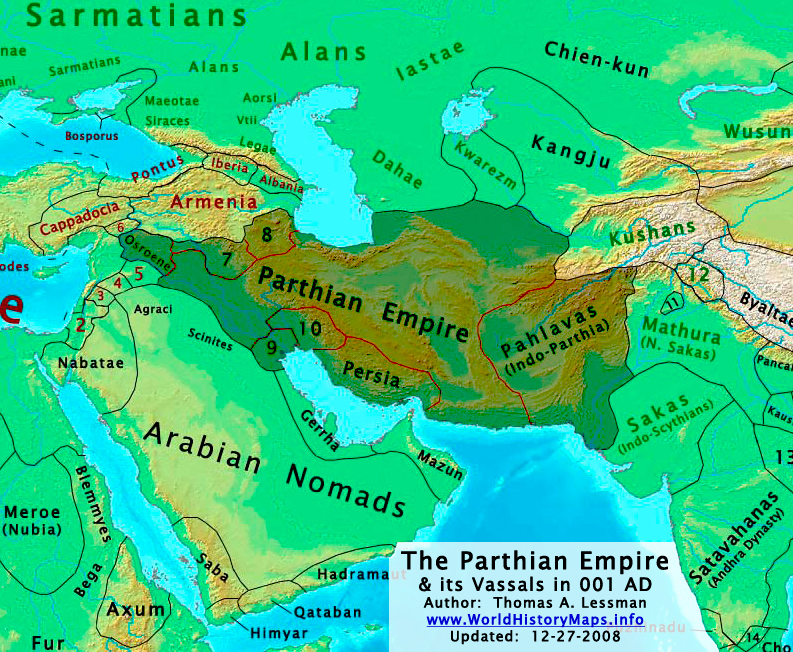
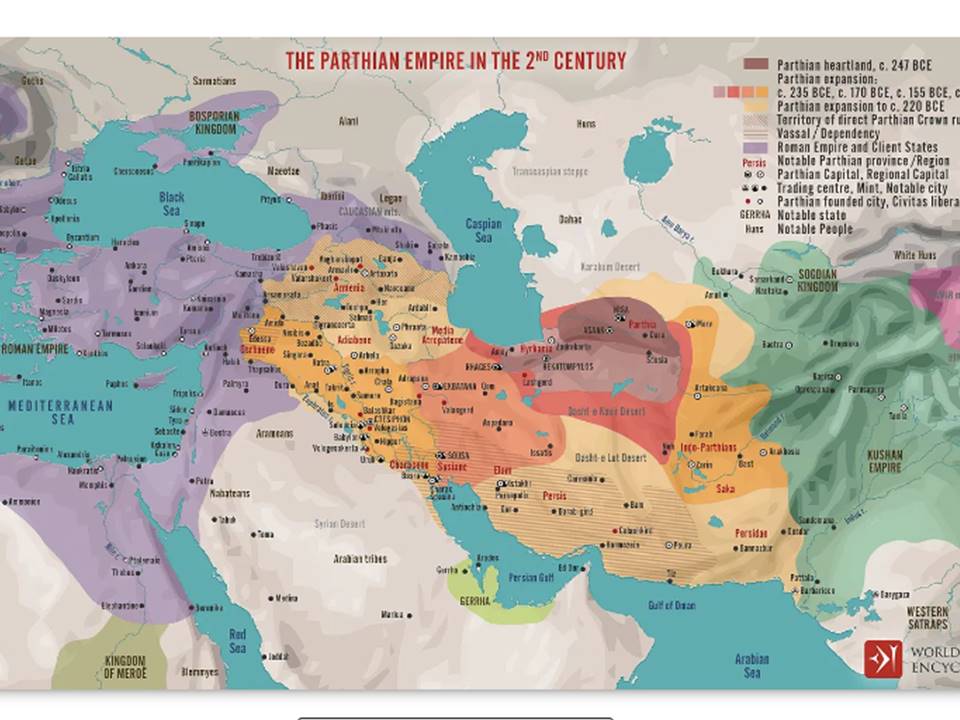
As one can understand easily, the de-Turanization of the Achaemenid period of Ancient Iran takes the form of a fallacious, radical, and extremist ‘Persianization’ of the Achaemenid Empire. However, this is refuted in many ways by the existing material record that pertains to the Achaemenid times; the Achaemenid onomastics, if duly studied, can reveal the presence of many Turanian names that are mistakenly now taken as ‘Persian’. The taxation of the Achaemenid satrapies reveals very well how greatly the court at Parsa (Persepolis) appreciated the provinces from where came most of the empire’s special military units, thus demanding lower taxation. And the military organization of the imperial army was originally conceived by typically nomadic fighters, and not by settled populations like the Babylonians or the Egyptians. The gradual decay of the Achaemenid Empire, viewed precisely in the light of the subsequent rise of the Arsacid Parthian kingdom, can also be explained as the consequence of the Turanian populations’ discontent with compromises made by the Achaemenid court with the ruthless Mithraic Magi.

Heavy taxation existed for India, Babylonia, Egypt and Western Anatolia, not for NE Iran and Central Asia, i.e. the lands where the bulk of Turanian populations lived.
Furthermore, the existing material record that pertains to the Iranian – Turanian History of later pre-Islamic and Islamic periods helps us also understand that the basic tenets of the historical evolution and the fundamental trends of daily life remained the same across millennia in Iran and Central Asia – in total rejection of the Orientalist fallacy and of the absurd Persianization of the Achaemenid Empire.
In fact, what happened at the times of the Barmak (Barmakian) noble and prestigious family in Abbasid Baghdad (8th – 9th c. CE), what occurred in the era of the Samanid (819-999) and Buyid (Buwayhi; 934-1062) dynasties, what constituted the splendid universe of Ferdowsi (940-1020), and what was attested in the Seljuk, Ilkhanid, Timurid, Ottoman and Safavid periods, did indeed characterize Achaemenid Iran, as a pre-Islamic Iranian–Turanian Empire.

The satrapies (provinces) of the Achaemenid Empire
The Iranians had an inclination to poetry, epics, literature, lyricism, arts and architecture, whereas the Turanians were known for their tendency to martial arts, military discipline and life, asceticism and spiritual exercises, mysticism and fables. The Turanians found it therefore normal to write in Old Achaemenid Iranian and in Aramaic in the 1st millennium BCE, in Syriac, Pahlavi and Middle Persian (Parsik) during the 1st millennium CE, and in Arabic and Farsi after the arrival of Islam.
The same pattern characterized Iranians and Turanians, Persians and Turkic nations, for millennia: if Babur, the formidable Timurid fighter, adventurous military leader, and founder of the Mughal Empire of South Asia, did not write his celebrated Babur-nameh in Chaghatay (Chagatai) Turkic, not a single linguistic vestige of the mother tongue of Genghis Khan would have been left down to our days. But this would not mean that Chagatai did not exist. About:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Immortals_(Achaemenid_Empire)
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Barmakids
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Samanid_Empire
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Buyid_dynasty
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ferdowsi
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Chagatai_Khanate
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Babur
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Baburnama
And it is this duality of the Iranian-Turanian Empire, this intertwined nature of the Iranian-Turanian people that great poets of the Islamic times repeatedly represented so illustratively in their verses. And who made more fun of the suggestion to write poetry in a Turkic language? None else but Nezami Ganjavi, a most illustrious Azeri, who has been rightfully considered as the national poet of Azerbaijan! About:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Nizami_Ganjavi
This is the way things functioned worldwide, when the post-Renaissance Western European academic-intellectual contamination had not affected the entire world. A well-diversified order existed in Islamic times, as per which Turkic languages were for the army and the military order, Farsi was for literary and artistic purposes, and Arabic (enriched tremendously thanks to Syriac Aramaic) was considered as the language of sciences. There was no division across what we call today national lines or ethnic borders because the notion of the nation was totally different and a widespread multilingualism existed in Asia, Africa and Eastern Europe.

Due to the multi-national, multi-lingual, multi-religious, and multi-cultural nature of the Achaemenid Empire, the then world’s largest state by far was not even named “Iran”, but Xšāça which means ‘universal order’. Actually, the Achaemenid Emperors of Iran and Turan never felt ‘ethnic Persians’. Following the millennia-long Ancient Akkadian and Assyrian–Babylonian universalism and imperial tradition, according to which the Assyrian Monarch was the ‘Emperor of the Universe’, the Achaemenids were ‘Kings of Kings’, because they viewed their realm, Iran and Turan, as definitely encompassing the entire Earth. No ethnic names mattered in the Iranian / Turanian Universalism. Actually, it may sound bizarre, but only under the Sassanids, so after 224 CE, was the Empire of the Shahanshahs named “Iran”. Never before! About:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Shah
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/King_of_Kings#Achaemenid_usage
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/King_of_the_Universe#List_of_known_Kings_of_the_Universe
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/King_of_Kings#Parthian_and_Sasanian_usage
Despite this fact, the disreputable Western universities and the Orientalist fallacy intentionally invented false terms to denote the Old Achaemenid language as a Persian language: ‘Old Persian’! This shameless distortion of a critical period of the History of Ancient Orient started with the overwhelming hysteria of ‘persianizing’ everything Iranian and Turanian. However, it soon became one of the pillars of the Western universities’ dogmatic and pseudo-scientific Talibanism.
The correct term for the language of the Achaemenid cuneiform inscriptions is ‘Old Iranian’, due to the fact that it evidently contains vocabulary from Western Iranian, Eastern Iranian, and Turanian languages.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Old_Persian
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Middle_Persian
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pahlavi_scripts
——————————————————–
FORTHCOMING
Turkey is Iran and Iran is Turkey
2500 Years of indivisible Turanian – Iranian Civilization distorted and estranged by Anglo-French Orientalists
By Prof. Muhammet Şemsettin Gözübüyükoğlu
(Muhammad Shamsaddin Megalommatis)
TABLE OF CONTENTS
PREFACE
CONTENTS
PART ONE. INTRODUCTION
CHAPTER I: A World held Captive by the Colonial Gangsters: France, England, the US, and the Delusional History Taught in their Deceitful Universities
A. Examples of fake national names
a) Mongolia (or Mughal) and Deccan – Not India!
b) Tataria – Not Russia!
c) Romania (with the accent on the penultimate syllable) – Not Greece!
d) Kemet or Masr – Not Egypt!
e) Khazaria – not Israel!
f) Abyssinia – not Ethiopia!
B. Earlier Exchange of Messages in Turkish
C. The Preamble to My Response
CHAPTER II: Geopolitics does not exist.
CHAPTER III: Politics does not exist.
CHAPTER IV: Turkey and Iran beyond politics and geopolitics: Orientalism, conceptualization, contextualization, concealment
A. Orientalism
B. Conceptualization
C. Contextualization
D. Concealment
PART TWO. EXAMPLE OF ACADEMICALLY CONCEALED, KEY HISTORICAL TEXT
CHAPTER V: Plutarch and the diffusion of Ancient Egyptian and Iranian Religions and Cultures in Ancient Greece
PART THREE. TURKEY AND IRAN BEYOND POLITICS AND GEOPOLITICS: REJECTION OF THE ORIENTALIST, TURKOLOGIST AND IRANOLOGIST FALLACIES ABOUT ACHAEMENID HISTORY
CHAPTER VI: The fallacy that Turkic nations were not present in the wider Mesopotamia – Anatolia region in pre-Islamic times
CHAPTER VII: The fallacious representation of Achaemenid Iran by Western Orientalists
CHAPTER VIII: The premeditated disconnection of Atropatene / Adhurbadagan from the History of Azerbaijan
CHAPTER IX: Iranian and Turanian nations in Achaemenid Iran
CHAPTER X: Iranian and Turanian Religions in Pre-Islamic Iran
PART FOUR. FALLACIES ABOUT THE SO-CALLED HELLENISTIC PERIOD, ALEXANDER THE GREAT, AND THE SELEUCID & THE PARTHIAN ARSACID TIMES
CHAPTER XI: Alexander the Great as Iranian King of Kings, the fallacy of Hellenism, and the nonexistent Hellenistic Period
CHAPTER XII: Parthian Turan: an Anti-Persian dynasty
CHAPTER XIII: Parthian Turan and the Philhellenism of the Arsacids
PART FIVE. FALLACIES ABOUT SASSANID HISTORY, HISTORY OF RELIGIONS, AND THE HISTORY OF MIGRATIONS
CHAPTER XIV: Arsacid & Sassanid Iran, and the wars against the Mithraic – Christian Roman Empire
CHAPTER XV: Sassanid Iran – Turan, Kartir, Roman Empire, Christianity, Mani and Manichaeism
CHAPTER XVI: Iran – Turan, Manichaeism & Islam during the Migration Period and the Early Caliphates
PART SIX. FALLACIES ABOUT THE EARLY EXPANSION OF ISLAM: THE FAKE ARABIZATION OF ISLAM
CHAPTER XVII: Iran – Turan and the Western, Orientalist distortions about the successful, early expansion of Islam during the 7th – 8th c. CE
CHAPTER XVIII: Western Orientalist falsifications of Islamic History: Identification of Islam with only Hejaz at the times of the Prophet
CHAPTER XIX: The fake, Orientalist Arabization of Islam
CHAPTER XX: The systematic dissociation of Islam from the Ancient Oriental History
PART SEVEN. THE FICTIONAL DIVISION OF ISLAM INTO ‘SUNNI’ AND ‘SHIA’
CHAPTER XXI: The fabrication of the fake divide ‘Sunni Islam vs. Shia Islam’
PART EIGHT. THE DISTORTED TERM ‘PERSIANATE’
CHAPTER XXII: The fake Persianization of the Abbasid Caliphate
PART NINE. FALLACIES ABOUT THE GOLDEN ERA OF THE ISLAMIC CIVILIZATION
CHAPTER XXIII: From Ferdowsi to the Seljuk Turks, Nizam al Mulk, Nizami Ganjavi, Jalal ad-Din Rumi and Haji Bektash
PART TEN. FALLACIES ABOUT THE TIMES OF TURANIAN (MONGOLIAN) SUPREMACY IN TERMS OF SCIENCES, ARTS, LETTERS, SPIRITUALITY AND IMPERIAL UNIVERSALISM
CHAPTER XXIV: From Genghis Khan, Nasir al-Din al Tusi and Hulagu to Timur
CHAPTER XXV: Timur (Tamerlane) as a Turanian Muslim descendant of the Great Hero Manuchehr, his exploits and triumphs, and the slow rise of the Turanian Safavid Order
CHAPTER XXVI: the Timurid Era as Peak of the Islamic Civilization, Shah Rukh, and Ulugh Beg, the Astronomer Emperor
PART ELEVEN. HOW AND WHY THE OTTOMANS, THE SAFAVIDS AND THE MUGHALS FAILED
CHAPTER XXVII: Ethnically Turanian Safavids & Culturally Iranian Ottomans: two identical empires that mirrored one another
CHAPTER XXVIII: Spirituality, Religion & Theology: the fallacy of the Safavid conversion of Iran to ‘Shia Islam’
CHAPTER XXIX: Selim I, Ismail I, and Babur
CHAPTER XXX: The Battle of Chaldiran (1514), and how it predestined the Fall of the Islamic World
CHAPTER XXXI: Ottomans, Safavids and Mughals: victims of their sectarianism, tribalism, theology, and wrong evaluation of the colonial West
CHAPTER XXXII: Ottomans, Iranians and Mughals from Nader Shah to Kemal Ataturk
PART TWELVE. CONCLUSION
CHAPTER XXXIII: Turkey and Iran beyond politics and geopolitics: whereto?
—————————————————
List of the already pre-published chapters of the book
Lines separate chapters that belong to different parts of the book.
CHAPTER VIII: The premeditated disconnection of Atropatene / Adhurbadagan from the History of Azerbaijan
CHAPTER X: Iranian and Turanian Religions in Pre-Islamic Iran
https://www.academia.edu/105664696/Iranian_and_Turanian_Religions_in_Pre_Islamic_Iran
—————————-
CHAPTER XI: Alexander the Great as Iranian King of Kings, the fallacy of Hellenism, and the nonexistent Hellenistic Period
CHAPTER XII: Parthian Turan: an Anti-Persian dynasty
https://www.academia.edu/52541355/Parthian_Turan_an_Anti_Persian_dynasty
CHAPTER XIII: Parthian Turan and the Philhellenism of the Arsacids
https://www.academia.edu/105539884/Parthian_Turan_and_the_Philhellenism_of_the_Arsacids
———————————
CHAPTER XIV: Arsacid & Sassanid Iran, and the wars against the Mithraic – Christian Roman Empire
CHAPTER XV: Sassanid Iran – Turan, Kartir, Roman Empire, Christianity, Mani and Manichaeism
CHAPTER XVI: Iran – Turan, Manichaeism & Islam during the Migration Period and the Early Caliphates
———————————-
CHAPTER XVII: Iran–Turan and the Western, Orientalist distortions about the successful, early expansion of Islam during the 7th-8th c. CE
CHAPTER XIX: The fake, Orientalist Arabization of Islam
https://www.academia.edu/105713891/The_fake_Orientalist_Arabization_of_Islam
CHAPTER XX: The systematic dissociation of Islam from the Ancient Oriental History
—————————————
CHAPTER XXI: The fabrication of the fake divide ‘Sunni Islam vs. Shia Islam’
https://www.academia.edu/55139916/The_Fabrication_of_the_Fake_Divide_Sunni_Islam_vs_Shia_Islam_
——————————————
CHAPTER XXII: The fake Persianization of the Abbasid Caliphate
https://www.academia.edu/61193026/The_Fake_Persianization_of_the_Abbasid_Caliphate
——————————————–
CHAPTER XXIII: From Ferdowsi to the Seljuk Turks, Nizam al Mulk, Nizami Ganjavi, Jalal ad-Din Rumi and Haji Bektash
————————————————
CHAPTER XXIV: From Genghis Khan, Nasir al-Din al Tusi and Hulagu to Timur
CHAPTER XXV: Timur (Tamerlane) as a Turanian Muslim descendant of the Great Hero Manuchehr, his exploits and triumphs, and the slow rise of the Turanian Safavid Order
CHAPTER XXVI: The Timurid Era as the Peak of the Islamic Civilization: Shah Rukh, and Ulugh Beg, the Astronomer Emperor
—————————————–
CHAPTER XXVII: Ethnically Turanian Safavids & Culturally Iranian Ottomans: two identical empires that mirrored one another
CHAPTER XXVIII: Spirituality, Religion & Theology: the fallacy of the Safavid conversion of Iran to ‘Shia Islam’
————————————————————
Download the chapter (text only) in PDF:
Download the chapter (with pictures and legends) in PDF: